The C-terminal extension of calprotectin mediates zinc chelation and modulates Staphylococcus aureus biomass accumulation
- PMID: 40944454
- PMCID: PMC12432413
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.70294
The C-terminal extension of calprotectin mediates zinc chelation and modulates Staphylococcus aureus biomass accumulation
Abstract
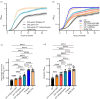
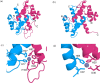
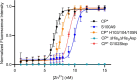
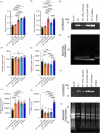
Calprotectin (CP) is an S100A8/S100A9 heterodimer that plays an important role in nutritional immunity at the host-microbe interface. CP combats Staphylococcus aureus growth by sequestration of zinc and other trace transition metals; however, questions remain about whether CP antimicrobial activity strictly relies on metal sequestration. Moreover, the precise mechanism for how zinc binds at the two distinct transition metal binding sites of CP is not known. High-resolution X-ray crystal structures reveal tetracoordinate binding in the canonical His3Asp site and hexacoordinate binding in the His6 site similar to the binding of manganese and nickel in this site. The S100A9 C-terminal extension (tail) contributes two of the His residues in the His6 metal-binding site, but measurements of zinc affinity show there is no significant reduction upon mutation of these His residues or deletion of the entire C-terminal tail. Bacterial growth and static biofilm assays show that the His mutations affect S. aureus biomass accumulation differently than loss of the S100A9 C-terminal tail, despite resulting in the same defect in bacterial-CP binding. These results reveal that the S100A9 tail of CP has a role in preventing S. aureus biomass accumulation.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; X‐ray crystallography; biofilm; calprotectin; nutritional immunity; zinc.
© 2025 The Author(s). Protein Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Protein Society.
Figures
References
-
- Abriat C, Enriquez K, Virgilio N, Cegelski L, Fuller GG, Daigle F, et al. Mechanical and microstructural insights of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli dual‐species biofilm at the air–liquid interface. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;188:110786. - PubMed
-
- Atkin KE, MacDonald SJ, Brentnall AS, Potts JR, Thomas GH. A different path: revealing the function of staphylococcal proteins in biofilm formation. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:1869–1872. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01AI138581/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007347/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI138581/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AI181344/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30AI181344/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101171/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI150701/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01145992/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007347/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127793/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127793/NH/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

