Initial leads to combat streptogramin resistance generated from X-ray fragment screening against VatD
- PMID: 40945513
- PMCID: PMC12435910
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2025.08.017
Initial leads to combat streptogramin resistance generated from X-ray fragment screening against VatD
Abstract
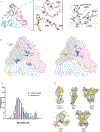
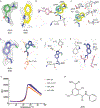
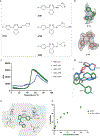
Streptogramins are potent antibiotics targeting bacterial ribosome. The synergistic binding of group A and B streptogramins to 50S-ribosome yields bactericidal effects. However, their efficacy is compromised by resistance mechanisms, including enzymatic acetylation of group A streptogramins by virginiamycin acetyltransferase (Vat) enzymes, which reduces their affinity for ribosomes. Using fragment-based drug discovery we identified starting points for development of VatD inhibitors. X-ray crystallography screening revealed three primary fragment-binding sites on VatD. In the acetyl-binding subsite, fragments stabilized distinct conformational states in critical residues, His82 and Trp121. In the antibiotic-binding site, two fragments formed interactions that could be leveraged for competitive inhibition. Elaborations of these fragments showed weak inhibition of VatD activity, indicating potential for further optimization. These findings establish initial hits that could restore streptogramin efficacy by targeting VatD directly, providing a structural foundation for inhibitor development against resistant bacterial strains.
Keywords: X-ray crystallography; acetyltransferase; antibiotic resistance; drug design; fragment based drug discovery.
Copyright © 2025 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.S.F. is a consultant to, shareholder of, and receives sponsored research support from Relay Therapeutics.
Figures
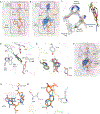

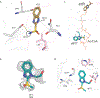

References
-
- Leclercq R, and Courvalin P (1998). Streptogramins: an answer to antibiotic resistance in gram-positive bacteria. Lancet 352, 591–592. - PubMed
-
- Hershberger E, Donabedian S, Konstantinou K, and Zervos MJ (2004). Quinupristin-dalfopristin resistance in gram-positive bacteria: mechanism of resistance and epidemiology. Clin Infect Dis 38, 92–98. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DN (2009). The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 44, 393–433. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

