Comparative Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1-RAs) in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Weight Management: A Real-World Data Study
- PMID: 40947139
- PMCID: PMC12433752
- DOI: 10.1002/pds.70214
Comparative Safety of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists (GLP-1-RAs) in Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Weight Management: A Real-World Data Study
Abstract
Purpose: This study assessed serious clinical outcomes comparing glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1-RAs) with sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2-Is) in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and patients without diabetes using two chronic weight management (CWM) regimens.
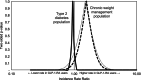
Methods: We performed a new user, active comparator cohort study in a large, national U.S. claims database. Adults who initiated GLP-1-RAs, SGLT2-Is, naltrexone/bupropion (NalBup), or phentermine/topiramate (PhenTop) from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2023 were included. Potential confounding was controlled using propensity score weighting for 82 clinical and demographic covariates, and risk ratios (RRs) were estimated.
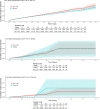
Results: This study included 330,684 GLP-1-RA users and 264,277 SGLT2-I users with T2DM. Among CWM patients without diabetes, we studied over 25,000 GLP-1-RA users, 5019 NalBup users, and 3841 PhenTop users. In both indications, GLP-1-RA users had higher rates of hospitalizations for gallbladder and biliary diseases with RRs ranging from 1.14 (95% CI: 1.06-1.22) in T2DM patients to 3.32 (95% CI: 1.44-7.64) in CWM patients. No reduction in the rate of cardiovascular events was observed for GLP-1-RA users with RRs ranging from 0.92 (95% CI: 0.37-2.25) in CWM patients to 1.03 (95% CI: 0.99-1.08) in T2DM patients. In T2DM patients, GLP-1-RA users had a lower rate of acute liver injury (RR: 0.76; 95% CI: 0.64-0.91).
Conclusions: This study corroborates an increased risk of hospitalization for gall bladder and biliary conditions among users of GLP-1-RAs and found similar rates as comparators of MI or stroke when GLP-1-RAs were used for T2DM or CWM. This real-world study complements placebo-controlled trials and can further inform prescribing decisions.
Protocol registration: The study protocol was pre-registered at the Center for Open Science's Real-World Evidence Registry and is publicly accessible online (https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/PSY74).
Keywords: GLP‐1‐RA; SGLT2; diabetes; naltrexone‐bupropion; phentermine‐topiramate; safety; weight management.
© 2025 Carelon Research Inc. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by
Figures

References
-
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration , “Byetta (Exenatide) Injection Approval,” (2005), https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2005/021773_byettatoc....
-
- Samson S. L., Vellanki P., Blonde L., et al., “American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Consensus Statement: Comprehensive Type 2 Diabetes Management Algorithm ‐ 2023 Update,” Endocrine Practice 29, no. 5 (2023): 305–340. - PubMed
-
- Niakan K. and Schock B., “GLP‐1 Agonists in Medicaid: Utilization, Growth, and Management,” (2024), https://www.milliman.com/‐/media/milliman/pdfs/2024‐articles/1‐18‐24_glp....
-
- Watanabe J. H., Kwon J., Nan B., and Reikes A., “Trends in Glucagon‐Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Use, 2014 to 2022,” Journal of the American Pharmacists Association (2003) 64, no. 1 (2024): 133–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

