Automated generation of epilepsy surgery resection masks: The RAMPS pipeline
- PMID: 40948604
- PMCID: PMC12423638
- DOI: 10.1162/IMAG.a.147
Automated generation of epilepsy surgery resection masks: The RAMPS pipeline
Abstract
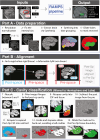
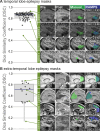
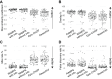
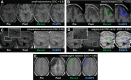
MRI-based delineation of brain tissue removed by epilepsy surgery can be challenging due to post-operative brain shift. In consequence, most studies use manual approaches which are prohibitively time-consuming for large sample sizes, require expertise, and can be prone to errors. We propose RAMPS (Resections And Masks in Preoperative Space), an automated pipeline to generate a 3D resection mask of pre-operative tissue. Our pipeline leverages existing software including FreeSurfer, SynthStrip, Sythnseg and ANTs to generate a mask in the same space as the patient's pre-operative T1 weighted MRI. We compare our automated masks against manually drawn masks and two other existing pipelines (Epic-CHOP and ResectVol). Comparing to manual masks (N = 87), RAMPS achieved a median (IQR) dice similarity of 0.86 (0.078) in temporal lobe resections, and 0.72 (0.32) in extratemporal resections. In comparison to other pipelines, RAMPS had higher dice similarities (N = 62) (RAMPS: 0.86, Epic-CHOP: 0.72, ResectVol: 0.72). We release a user-friendly, easy-to-use pipeline, RAMPS, open source for accurate delineation of resected tissue.
Keywords: epilepsy; mask; resection; surgery; volume.
© 2025 The Authors. Published under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed, B., Brodley, C. E., Blackmon, K. E., Kuzniecky, R., Barash, G., Carlson, C., Quinn, B. T., Doyle, W., French, J., Devinsky, O., & Thesen, T. (2015). Cortical feature analysis and machine learning improves detection of “MRI-negative” focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsy & Behavior, 48, 21–28. 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.04.055 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold, T. C., Muthukrishnan, R., Pattnaik, A. R., Sinha, N., Gibson, A., Gonzalez, H., Das, S. R., Litt, B., Englot, D. J., Morgan, V. L., Davis, K. A., & Stein, J. M. (2022). Deep learning-based automated segmentation of resection cavities on postsurgical epilepsy MRI. NeuroImage: Clinical, 36, 103154. 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103154 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Billardello, R., Ntolkeras, G., Chericoni, A., Madsen, J. R., Papadelis, C., Pearl, P. L., Grant, P. E., Taffoni, F., & Tamilia, E. (2022). Novel user-friendly application for MRI segmentation of brain resection following epilepsy surgery. Diagnostics, 12, 1017. 10.3390/diagnostics12041017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Billot, B., Greve, D. N., Puonti, O., Thielscher, A., Van Leemput, K., Fischl, B., Dalca, A. V., Iglesias, J. E., & ADNI. (2023). SynthSeg: Segmentation of brain MRI scans of any contrast and resolution without retraining. Medical Image Analysis, 86, 102789. 10.1016/j.media.2023.102789 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
