Structural Characterizations and In Vitro Bioactivities of a d‑Fructose-Rich Polysaccharide from Gymnopetalum cochinchinense as a Potential Candidate for Alleviating Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 40949219
- PMCID: PMC12423878
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05628
Structural Characterizations and In Vitro Bioactivities of a d‑Fructose-Rich Polysaccharide from Gymnopetalum cochinchinense as a Potential Candidate for Alleviating Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
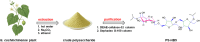
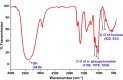
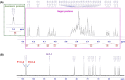
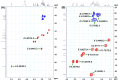
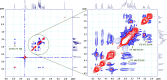
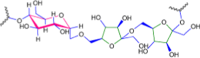
The presented investigation attempts to unveil the structural characteristics, bioactivities, and potential application of Gymnopetalum cochinchinense-derived d-fructose-rich heteropolysaccharide (denoted as PS-HB5) for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Structural analyses of the PS-HB5 evaluated by FT-IR, GC-MS, and NMR techniques reveal a novel repeating unit composed of d-glucose and d-fructose linked through (1 → 6)-glucosyl, (2 → 6)-fructosyl, and (2 → 4)-fructosyl bonds, and possesses a molecular weight of 1.217 × 105 Da. The PS-HB5 exhibits strong antioxidant activity, as evidenced by its DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging rates of 84.12% and 74.14%, associated with the IC50 values of 0.80 and 3.06 mg.mL-1, respectively. In addition, the PS-HB5 shows an inhibition rate of 78.37% (IC50 = 221.96 μg.mL-1) toward nitric oxide (NO) production in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Cytotoxicity assays indicate selective inhibition of the PS-HB5 against HepG2 and KB cancer cell lines (IC50 = 449.95 and 408.34 μg/mL), with minimal impact on MCF-7 and SK-LU-1. Interestingly, PS-HB5 demonstrates an outstanding AChE inhibitory effect, achieving 41.01% inhibition at 500 μg.mL-1, placing it among the most active AChE-inhibitory polysaccharides. These findings unveil the PS-HB5 potential as a candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures




References
-
- Cai Y., Li Y., Wang Y., Xu Y., Chen T., Xue R., Liu Y., Chen W., Yang X., Liu Z., Bao X., Huang Z.. Triple-mode sensing platform for acetylcholinesterase activity monitoring and anti-Alzheimer’s drug screening based on a highly stable Cu (I) compound. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025;271:117078. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.117078. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
