This is a preprint.
Tractor Workflow Pipeline: A Scalable Nextflow Framework for Local Ancestry-Aware Genome-Wide Association Studies
- PMID: 40950129
- PMCID: PMC12424779
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.09.02.673402
Tractor Workflow Pipeline: A Scalable Nextflow Framework for Local Ancestry-Aware Genome-Wide Association Studies
Abstract
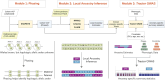
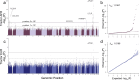
The routine exclusion of admixed individuals from traditional Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS) due to concerns about spurious associations has hindered genetic analyses involving multiple ancestries. Tractor GWAS addresses this issue by incorporating local ancestry into its analysis, empowering identification of ancestry-enriched hits and generating ancestry-specific summary statistics. However, Tractor requires accurate genomic phasing and local ancestry inference as prerequisite steps, which requires additional bioinformatics expertise and decision points regarding reference panel setup. To streamline, harmonize, and automate this process, we present a scalable Nextflow workflow that integrates all necessary steps, minimizing the need for manual intervention while remaining modular and customizable. The workflow supports multiple commonly used tools and offers flexibility in how Tractor is implemented. To demonstrate its utility, we applied this pipeline to analyze 32 blood biomarkers in 6,245 two-way AFR-EUR admixed individuals from the UK Biobank. This pipeline ran efficiently at scale, replicated known associations, and identified novel ancestry-specific loci. These novel associations were largely driven by variants present on African ancestral tracts but absent from European tracts, underscoring the value of local ancestry-aware methods in uncovering previously missed genetic signals. By enabling the efficient analysis of admixed individuals, our workflow facilitates Tractor use, paving the way for more broader genetic discovery.
Figures
References
-
- Atkinson E.G. et al. (2022) Cross-ancestry genomic research: time to close the gap. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 1–2.
-
- Bergström A. et al. (2020) Insights into human genetic variation and population history from 929 diverse genomes. Science (1979), 367. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
