Genome-wide pleiotropy analysis of longitudinal blood pressure and harmonized cognitive performance measures
- PMID: 40951946
- PMCID: PMC12434708
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70681
Genome-wide pleiotropy analysis of longitudinal blood pressure and harmonized cognitive performance measures
Abstract
Introduction: Identifying pleiotropy for blood pressure (BP) and cognitive performance measures may indicate mechanistic links between hypertension and Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods: We performed a pleiotropy genome-wide association study (GWAS) for paired measures of systolic, diastolic, pulse, and mean arterial pressure with memory, executive function, and language scores using 116,075 exam data from 25,726 participants in clinic-based and prospective cohorts. Significant findings were evaluated by Bayesian colocalization and differential gene expression in brain tissue from pathologically confirmed AD cases with and without clinical symptoms.
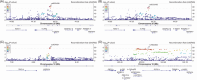
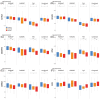
Results: Genome-wide significant pleiotropy for BP and cognitive performance with JPH2, GATA3, PAX2, LOC105371656, and SUFU in the total sample; RTN4, ULK2, SORBS2, and LOC100128993 in prospective cohorts; and ADAMTS3 and LINC02946 in clinic-based cohorts. Six pleiotropic loci influence cognition directly, and six genes were differentially expressed between pathologically confirmed AD cases with and without antemortem cognitive impairment.
Discussion: Our results provide insight into mechanisms underlying hypertension and AD.
Highlights: Genome-wide significant pleiotropy in blood pressure (BP) and cognitive performance measures were identified with 11 novel loci: JPH2, GATA3, PAX2, LOC105371656, SUFU in the total sample; RTN4, ULK2, SORBS2, LOC100128993 in prospective cohorts; and ADAMTS3, LINC02946 in clinic-based cohorts. SUFU, RTN4, SORBS2, ADAMTS3, and GATA3 affected cognition directly rather than through BP. ACTR1A, HIF1AN, ADAMTS3, RTN4, SORBS2, and SUFU at pleiotropic loci were differentially expressed among controls and pathologically confirmed AD cases with and without clinical symptoms.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; blood pressure; cognitive domain score; differential gene expression; genome‐wide association study; longitudinal study; pathway analysis; pleiotropy.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
L.A.F. received support from NIH grants and an honorarium for serving as a journal editor. T.H. serves on the advisory board for Vivid Genomics, deputy editor for Alzheimer's & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions, and senior associate editor for Alzheimer's & Dementia. L.‐S.W. received honoraria for several lectures. None of the other authors have conflicts of interest to disclose. T.J.H. serves as a consultant for Circular Genomics and on the editorial board of multiple journals, owns stock in Vivid Genomics, and received travel support from the Alzheimer's Association. G.D.S. received an honorarium for serving on an external advisory board. AJS serves on advisory boards for Siemens Medical Solutions, Eisai Pharmaceuticals and Novo Nordisk, on a monitoring board and external advisory committees for NIH, and as Editor‐in‐Chief for
Figures

Update of
-
Genome-wide pleiotropy analysis of longitudinal blood pressure and harmonized cognitive performance measures.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 13:2025.02.11.25322014. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.11.25322014. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Sep;21(9):e70681. doi: 10.1002/alz.70681. PMID: 39990565 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 AG072975/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24-AG074855/Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project Phenotype Harmonization Consortium
- U01 AG068057/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54-AG052427/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG17917/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- R01 AG059716/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG72975/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- U01 AG081230/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG10161/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- U01-AG062602/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG082665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1-AG057519/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG058654/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AG052427/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG058654/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG048927/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG068057/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG059716/Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project Phenotype Harmonization Consortium
- U01 AG061356/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AG15819/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- U24 AG074855/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG61356/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- U24-AG021886/National Cell Repository for Alzheimer's Disease
- U01-AG082665/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG041689/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG068057/Alzheimer's Disease Sequencing Project Phenotype Harmonization Consortium
- U01-AG46152/University of Pennsylvania, funded by NIA, and the Religious Orders Study/Rush Memory and Aging Project
- R01-AG059716/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG032984/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U24-AG041689/National Institute on Aging Genetics of Alzheimer's Disease Data Storage Site
- U01 AG062602/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG081230/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048927/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AG072878/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057519/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AG081230/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24-AG074855/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U19-AG068753/GF/NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG068753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

