IV Immunoglobulin Is Associated With Epigenetic, Ribosomal, and Immune Changes in Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome
- PMID: 40953324
- PMCID: PMC12440302
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200467
IV Immunoglobulin Is Associated With Epigenetic, Ribosomal, and Immune Changes in Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome
Abstract
Objectives: Pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS) is characterized by infection-provoked abrupt-onset obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) and neurodevelopmental regression. Owing to the neuroimmune hypothesis, we investigated the effects of IV immunoglobulin (IVIg) on cell-specific gene expression.
Methods: Single-cell RNA sequencing of peripheral immune cells was performed in 5 children with PANS (median age 8 (5.5-16) years), before and after administering open-label IVIg, compared with 4 controls (median age 13.5 [IQR 12-15] years).
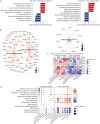
Results: The index PANS event (age 1.8-13 years) involved abrupt eating restriction (n = 5), developmental regression (n = 4), and OCD (n = 3). A total of 144,470 cells were sequenced and clustered into 11 cell types. Children with PANS before IVIg compared with controls showed downregulated immune pathways (defense response, innate immunity, secretory granules) in most cell types, with natural killer (NK) cells showing upregulated immune pathways (response to corticosteroid), supporting baseline "immune dysregulation." Ribosomal pathways were upregulated in neutrophils and CD8 T cells but downregulated in NK cells. In children with PANS after IVIg, the baseline immune and ribosomal pathway abnormalities were reversed and histone modification pathways (histone methyltransferase, chromatin) were downregulated in neutrophils and NK cells.
Discussion: We propose that PANS is an epigenetic immune brain disorder with cellular epigenetic, ribosomal, and immune dysregulation. Epigenetic and immune-modulating therapies, such as IVIg, may have disease-modifying effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures

References
-
- Nishida H, Han VX, Keating BA, et al. Chromatin, transcriptional and immune dysregulation in children with neurodevelopmental regression. medRxiv. 2025. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.05.25322433 - DOI
-
- Johnson M, Ehlers S, Fernell E, Hajjari P, Wartenberg C, Wallerstedt SM. Anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and immunomodulatory treatment in children with symptoms corresponding to the research condition PANS (Pediatric Acute-onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome): a systematic review. PLoS One. 2021;16(7):e0253844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253844 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
