A Novel Genetic TDP-43 Pig Model Mimics Multiple Key ALS-Like Features
- PMID: 40959204
- PMCID: PMC12434190
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.70330
A Novel Genetic TDP-43 Pig Model Mimics Multiple Key ALS-Like Features
Abstract
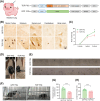
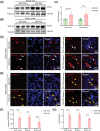
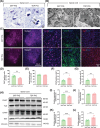
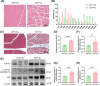
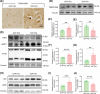
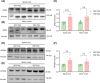
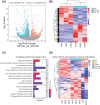
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that lacks ideal models to comprehensively recapitulate its pathological features. TDP-43 pathology, a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, plays a critical role in disease progression. Given the anatomical and physiological similarities between pig and human brains, large animal models offer a unique advantage in more accurately simulating patient-specific disease characteristics. In this study, we rapidly established a TDP-43-induced neurodegenerative disease model in pigs through ear vein injection of the TDP-43M337V virus. Disease progression was systematically evaluated using behavioral assessments and pathological analyses. This porcine model produced extremely severe motor dysfunction accompanied by significant muscle atrophy and fibrosis. Additionally, characteristic TDP-43 pathological phenotypes were observed, including degeneration of spinal motor neurons and proliferation of glial cells in both the brain and spinal cord. Notably, TDP-43M337V induction led to a significant upregulation of TMEM106B, SOD1, and APOE4 levels. This TDP-43 porcine model recapitulates multiple key features of ALS and serves as a valuable complement to existing animal models, providing a robust platform for investigating TDP-43-related pathogenic mechanisms of TDP-43 and developing effective therapeutics.
Keywords: APOE4; SOD1; TDP‐43; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; movement disorder; pig model.
© 2025 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Brown R. H. and Al‐Chalabi A., “Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis,” New England Journal of Medicine 377, no. 2 (2017): 162–172. - PubMed
-
- Xu L., Liu T., Liu L., et al., “Global Variation in Prevalence and Incidence of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis,” Journal of Neurology 267, no. 4 (2020): 944–953. - PubMed
-
- Rosen D. R., Siddique T., and Patterson D., “Mutations in Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Gene Are Associated With Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis,” Nature 362, no. 6415 (1993): 59–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
