O-GlcNAcylated Hsp47 as a predictive biomarker in colorectal cancer: Kaempferol targets OGT-collagen axis for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 40959291
- PMCID: PMC12435574
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.116513
O-GlcNAcylated Hsp47 as a predictive biomarker in colorectal cancer: Kaempferol targets OGT-collagen axis for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
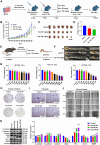
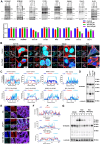
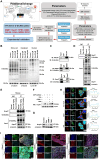
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a highly lethal gastrointestinal malignancy, and its progression is closely related to abnormal protein O-GlcNAcylation modifications, especially during extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. Kaempferol is a natural flavonoid with medicinal value that can inhibit CRC progression through various pathways. However, it is unclear whether its mechanism of action involves O-GlcNAc-driven metabolic reprogramming. This study confirmed that kaempferol can significantly inhibit CRC growth both in vitro and in vivo and effectively reduce the overall protein O-GlcNAcylation levels. Mechanistic studies indicate that kaempferol reduces the levels of substrate uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) and downregulates the expression of O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT), thereby decreasing the O-GlcNAcylation levels of proteins. This leads to a reduction in the O-GlcNAc modification of downstream heat shock protein 47 (Hsp47), which in turn affects the expression and intracellular localization of Hsp47, ultimately inhibiting the maturation and secretion of type I collagen, thereby blocking CRC progression. This study reveals a new mechanism by which kaempferol inhibits CRC by targeting the O-GlcNAcylation pathway. The study results suggest that O-GlcNAc-modified Hsp47 could serve as a potential therapeutic target for CRC and propose a treatment strategy guided by flavonoid biomarkers based on the inhibition of the OGT-collagen axis.
Keywords: Colorectal Cancer; Hsp47; Kaempferol; O-GlcNAc; OGT.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Linlin Lu reported receiving funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China during the conduct of the study. Zhongqiu Liu also reported receiving funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China during the study. No funding was reported by the other authors.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023 Jan;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
-
- Ma J, Wu C, Hart GW. Analytical and Biochemical Perspectives of Protein O-GlcNAcylation. Chem Rev. 2021;121(3):1513–1581. - PubMed
-
- Pinho SS, Reis CA. Glycosylation in cancer: mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(9):540–555. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

