GALNTL5 binds GalNAc and is required for migration through the uterotubal junction and sperm-zona pellucida binding
- PMID: 40962834
- PMCID: PMC12443989
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63805-4
GALNTL5 binds GalNAc and is required for migration through the uterotubal junction and sperm-zona pellucida binding
Abstract
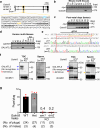
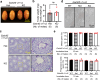
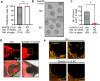
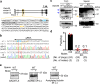
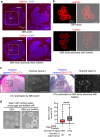
More than 20 genes expressed in the male reproductive tract have been identified as essential factors for sperm migration to and through the utero-tubal junction (UTJ), and they are divided into ADAM3-dependent and ADAM3-independent pathways. In parallel, sperm having UTJ migration defects also show impaired binding to the zona pellucida (ZP). Herein, we demonstrate that knockout of Galntl5, encoding a sperm surface protein, causes impaired sperm binding with the UTJ and ZP, and null males have severe infertility. GALNTL5 appreciably disappears in sperm lacking Adam3 or Lypd4, required for ADAM3-dependent and ADAM3-independent pathways, and GALNTL5 binds to N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) distributed on the UTJ and ZP. Blockage of GalNAc decreases the number of sperm binding to the UTJ and ZP. Thus, we unveil that GALNTL5 is a responsible factor for UTJ migration and sperm-ZP binding, and that sperm bind to the UTJ and ZP through interaction of GALNTL5 and GalNAc.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Lillie, F. R. The mechanism of fertilization. Science38, 524–528 (1913). - PubMed
-
- Wassarman, P. M. Zona pellucida glycoproteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem.57, 415–442 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Wassarman, P. M. Towards molecular mechanisms for gamete adhesion and fusion during mammalian fertilization. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.7, 658–664 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Bleil, J. D. & Wassarman, P. M. Mammalian sperm-egg interaction: identification of a glycoprotein in mouse egg zonae pellucidae possessing receptor activity for sperm. Cell20, 873–882 (1980). - PubMed
-
- Rankin, T. et al. Mice homozygous for an insertional mutation in the Zp3 gene lack a zona pellucida and are infertile. Development122, 2903–2910 (1996). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JP21H05033/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP20H03172/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP22H04922 (AdAMS)/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- R01 HD088412/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- JP25KJ1979/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP25K02196/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23K20043/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JP23jf0126001/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- JPMJPR2148/MEXT | JST | Precursory Research for Embryonic Science and Technology (PRESTO)
- R01HD088412/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- JPMJCR21N1/MEXT | JST | Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology (CREST)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

