This is a preprint.
Multiple clades of regulators contribute to bacterial phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis
- PMID: 40964295
- PMCID: PMC12439885
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.09.08.674922
Multiple clades of regulators contribute to bacterial phosphate homeostasis and pathogenesis
Abstract
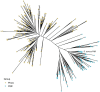
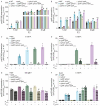
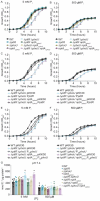
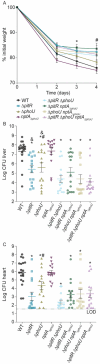
Phosphate is both essential for life and toxic, necessitating the tight regulation of its acquisition. Based on Escherichia coli, most bacteria are thought to use a single accessory protein that monitors import to regulate phosphate homeostasis. This work reveals that most bacteria possess multiple distinct families of accessory regulators with each family regulating homeostasis in conjunction with a unique importer family. The antibiotic-resistant pathogen Staphylococcus aureus can obtain phosphate from divergent environments and possesses accessory-transporter pairs from all three identified groups. Investigations with S. aureus revealed that all three accessory proteins can regulate phosphate homeostasis, but that there is a hierarchy, which is dictated by the environment. Multiple accessory regulators are independently necessary for S. aureus to cause infection. Thus, microbes possess not one, but multiple distinct groups of accessory regulatory proteins and this diversity enables them to control phosphate homeostasis across environments, including those encountered during infection.
Keywords: PhoPR; PhoU; Staphylococcus aureus; phosphate homeostasis; regulation; two-component system; virulence.
Figures

References
-
- Bruna RE, Kendra CG, Groisman EA, Pontes MH. Limitation of phosphate assimilation maintains cytoplasmic magnesium homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118, (2021).
-
- Webb DC, Rosenberg H, Cox GB. Mutational analysis of the Escherichia coli phosphate-specific transport system, a member of the traffic ATPase (or ABC) family of membrane transporters. A role for proline residues in transmembrane helices. J Biol Chem 267, 24661–24668 (1992). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
