Rasch analysis of the NEI-VFQ-25: vision-related quality of life in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy after lenadogene nolparvovec gene therapy
- PMID: 40967677
- PMCID: PMC12458720
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjophth-2025-002164
Rasch analysis of the NEI-VFQ-25: vision-related quality of life in Leber hereditary optic neuropathy after lenadogene nolparvovec gene therapy
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the suitability of the National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI-VFQ-25) for measuring vision-related quality of life (VRQoL) in patients with Leber hereditary optic neuropathy receiving lenadogene nolparvovec gene therapy in three Phase III randomised controlled clinical trials.
Methods: VRQoL was assessed using the NEI-VFQ-25 at baseline (n=174) and 2 years after treatment (n=152). All participants received lenadogene nolparvovec in at least one eye. The scoring structure of the original NEI-VFQ-25 was evaluated for fit to the Rasch model, and a post hoc revision was created and psychometrically reevaluated. Stacked analysis was conducted to compare Rasch-revised scores at baseline and 2 years after treatment.
Results: The original NEI-VFQ-25 exhibited multiple issues including limitations in response functioning and scale dimensionality. These issues were rectified by revising the NEI-VFQ25 into two separate unidimensional scales measuring 'Vision-related Activity Limitation' (VAL) and 'Socioemotional Functioning' (SEF). Participants' mean VAL score at baseline on a Rasch-transformed 0-100 scale was 46.1 (11.7), improving to 48.4 (13.7) after treatment (F(1, 324) = 2.67, p=0.103). On the SEF scale, there was a significant difference 2 years after treatment, with participants improving from a mean score of 40.1 (14.1) at baseline to 49.6 (17.6) (F(1, 324) = 29.1, p<0.001).
Conclusions: The scoring structure of the original NEI-VFQ-25 has limitations that undermine its psychometric validity as a measure of VRQoL. Using the Rasch-revised NEI-VFQ-25, we determined that improvement in VRQoL after treatment with lenadogene nolparvovec was driven predominantly by an improvement in socioemotional functioning.
Keywords: Clinical Trial; Genetics; Optic Nerve; Treatment Medical.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MT is an employee of GenSight Biologics. PYWM is a consultant for GenSight Biologics and Stealth BioTherapeutics and has received research support from GenSight Biologics and Santhera Pharmaceuticals.
Figures
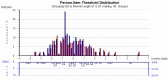
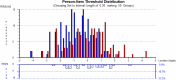
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
