Unusual Complication of Percutaneous Gastrostomy Tube Replacement
- PMID: 40970177
- PMCID: PMC12443151
- DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000001834
Unusual Complication of Percutaneous Gastrostomy Tube Replacement
Abstract
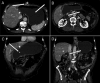
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes are commonly used for long-term nutritional support in patients with impaired swallowing due to neurological conditions, malignancy, or critical illness. Although placement, removal, and replacement are generally safe, complications may occur. We report a case of complete gastric outlet obstruction due to unusually deep percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube insertion during replacement in a 63-year-old man with esophageal cancer. Symptoms resolved after repositioning the tube. This case highlights the need for proper training and postreplacement verification to ensure safe outcomes.
Keywords: PEG; gastric outlet obstruction; percutaneous gastrostomy tube.
Written work prepared by employees of the Federal Government as part of their official duties is, under the U.S. Copyright Act, a “work of the United States Government” for which copyright protection under Title 17 of the United States Code is not available. As such, copyright does not extend to the contributions of employees of the Federal Government.
Figures
References
-
- Sealock RJ, Munot K. Common gastrostomy feeding tube complications and troubleshooting. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1864–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

