Free water predicts dementia with Lewy bodies in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder
- PMID: 40970479
- PMCID: PMC12447249
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.70570
Free water predicts dementia with Lewy bodies in isolated REM sleep behavior disorder
Abstract
Introduction: Most individuals with isolated rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder (iRBD) develop dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) or Parkinson's disease (PD). Brain biomarkers predicting specific phenoconversion trajectories are lacking.
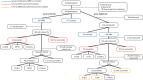
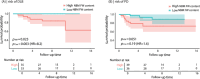
Methods: In this multicenter diffusion magnetic resonance imaging study (261 iRBD, 177 controls), free water (FW) was measured in the nucleus basalis of Meynert (NBM) and posterior substantia nigra (SN). Among 230 iRBD patients with follow-up, 64 converted (16 DLB, 38 PD). Time-to-event analyses were performed to assess differential phenoconversion.
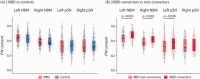
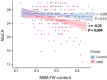
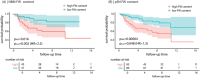
Results: Phenoconverters had higher FW in the NBM and posterior SN. Only FW in the NBM predicted conversion to DLB over PD. NBM volume predicted DLB conversion, but only FW remained significant when both were modeled. FW in the NBM correlated with lower MoCA scores in iRBD.
Discussion: FW in the NBM is a sensitive biomarker of cognitive decline and DLB progression in iRBD, outperforming volume and supporting its use in early stratification.
Highlights: FW in the NBM specifically identifies conversion to DLB. Increased FW in the NBM is associated with lower global cognition in iRBD. FW in the SN in iRBD does not relate more to DLB than PD. FW in the NBM is a biomarker of differential phenoconversion in iRBD.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease; REM sleep behavior disorder; biomarker; dementia with Lewy bodies; diffusion magnetic resonance imaging; free water; prognosis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Author disclosures are available in the Supporting Information.
Figures
References
-
- Hogl B, Stefani A, Videnovic A. Idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder and neurodegeneration—an update. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(1):40‐55. - PubMed
-
- Galbiati A, Verga L, Giora E, Zucconi M, Ferini‐Strambi L. The risk of neurodegeneration in REM sleep behavior disorder: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of longitudinal studies. Sleep Med Rev. 2019;43:37‐46. - PubMed
-
- Rahayel S, Tremblay C, Vo A, et al. Brain atrophy in prodromal synucleinopathy is shaped by structural connectivity and gene expression. Brain. 2022;145(9):3162‐3178. - PubMed
-
- Rahayel S, Postuma RB, Montplaisir J, et al. A prodromal brain‐clinical pattern of cognition in synucleinopathies. Ann Neurol. 2021;89(2):341‐357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- Roche
- Parkinson's Foundation
- Michael J. Fox Foundation
- R. Howard Webster Foundation
- International Parkinson and Movement Disorders Society
- PPG-2023-0000000122/Parkinson Canada
- 0000000082/Alzheimer Society Canada
- ANR-10-IAIHU-06/Programme d'investissements d'avenir
- IAIHU-06/Paris Institute of Neurosciences-IHU
- ANR-11-INBS-0006/Agence Nationale de la Recherche
- Électricité de France
- Fondation d'Entreprise EDF
- Biogen Inc.
- Fonds Saint-Michel
- Société Française de Médecine Esthétique
- Institut de France
- Fonds de recherche du Québec-Santé
- W. Garfield Weston Foundation
- NIH/National Institute on Aging
- J-2101/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC)
- NU21-04-00535/Czech Health Research Council
- LX22NPO5107/Czech Health Research Council
- 4D Pharma
- AbbVie Inc.
- AcureX Therapeutics
- Allergan
- Aligning Science Across Parkinson's (ASAP)
- Avid Radiopharmaceuticals
- Bial Biotech
- BioLegend
- Bristol Myers Squibb
- Calico Life Sciences LLC
- Celgene Corporation
- DaCapo Brainscience
- Denali Therapeutics
- Edmond J. Safra Foundation
- Eli Lilly and Company
- GE Healthcare
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Golub Capital
- Handl Therapeutics
- Insitro
- LLC
- Piramal Imaging
- Prevail Therapeutics
- F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd.
- Genentech Inc.
- Teva Neuroscience, Inc.
- Vanqua Bio
- Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
- Yumanity Therapeutics, Inc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

