A long-term ketogenic diet causes hyperlipidemia, liver dysfunction, and glucose intolerance from impaired insulin secretion in mice
- PMID: 40971428
- PMCID: PMC12448075
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adx2752
A long-term ketogenic diet causes hyperlipidemia, liver dysfunction, and glucose intolerance from impaired insulin secretion in mice
Abstract
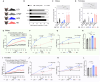
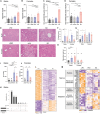
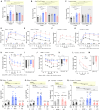
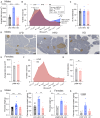
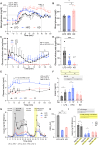
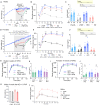
Ketogenic diets (KDs)-very-low-carbohydrate and very-high-fat diets-have gained popularity as therapeutic against obesity and type 2 diabetes. However, their long-term effects on metabolic health remain understudied. Here, we show that, in male and female mice, a KD protects against weight gain and induces weight loss but over time leads to the development of hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, and severe glucose intolerance. Unlike mice on conventional high-fat diet, KD-fed mice remain insulin sensitive and display low-insulin levels. Hyperglycemic clamp and ex vivo glucose-stimulated insulin secretion assays revealed systemic and cell-intrinsic impairments in insulin secretion. Transcriptomic profiling of islets from KD-fed mice indicated endoplasmic reticulum (ER)/Golgi stress and disrupted ER-Golgi protein trafficking, which were confirmed by electron microscopy showing a dilated Golgi network consistent with defective insulin granule trafficking and secretion. Together, these results suggest that long-term KD leads to multiple aberrations of metabolic parameters that caution their systematic use as a health-promoting dietary intervention.
Figures

Update of
-
Long-term ketogenic diet causes hyperlipidemia, liver dysfunction, and glucose intolerance from impaired insulin trafficking and secretion in mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 17:2024.06.14.599117. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.14.599117. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Sep 19;11(38):eadx2752. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adx2752. PMID: 38948738 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Kossoff E. H., Zupec-Kania B. A., Amark P. E., Ballaban-Gil K. R., Bergqvist A. G. C., Blackford R., Buchhalter J. R., Caraballo R. H., Cross J. H., Dahlin M. G., Donner E. J., Klepper J., Jehle R. S., Kim H. D., Liu Y. M. C., Nation J., Nordli D. R. Jr., Pfeifer H. H., Rho J. M., Stafstrom C. E., Thiele E. A., Turner Z., Wirrell E. C., Wheless J. W., Veggiotti P., Vining E. P. G., Charlie Foundation, Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society, Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society, International Ketogenic Diet Study Group , Optimal clinical management of children receiving the ketogenic diet: Recommendations of the International Ketogenic Diet Study Group. Epilepsia 50, 304–317 (2009). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

