Analysis of the influence of coupling agents on the composition of artificial rocks with polymer matrix
- PMID: 40973742
- PMCID: PMC12449475
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-18783-4
Analysis of the influence of coupling agents on the composition of artificial rocks with polymer matrix
Abstract
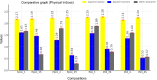
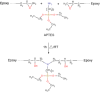
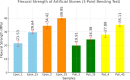
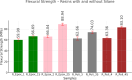
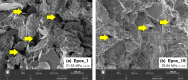
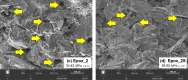
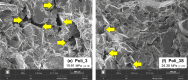
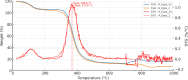
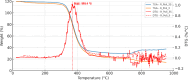
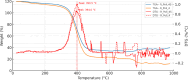
While advances in material improvement are significant, actual adoption still depends on balancing cost, environmental impact, and performance. High-specification chemicals and complex processes can increase production costs, and the sustainability of new, partially synthetic systems must be examined. In this context, this study explored an alternative approach for agglomerated rocks, where the use of coupling agents enhances interface engineering. We addressed the mineral-polymer relationship by comparing two epoxy resins and two polyester resins with and without silane-based coupling agents (γ-APS for epoxies; MPTS for polyesters) in 85% by weight of granite waste. Original contributions include: a mix design selection (simplex network) for the densest packing (grain size: 66% coarse, 17% medium, 17% fine) by vibrated bulk density, validated via ANOVA/Tukey; a unified manufacturing route using vibropressing, vacuum compaction, and vacuum hot pressing (600 mmHg, 10 MPa, 90 °C). Physical indices (bulk density, open porosity, and water absorption) were evaluated in accordance with ABNT NBR 15845-2. Three-point bending tests were performed using ABNT NBR 15845-6 (for slabs) and ASTM D790 (for neat resins). Thermal behavior and fracture micromechanics were assessed through TGA/DSC (ASTM D6370) and SEM. Silanes increased bulk density and drastically reduced porosity and water absorption (by 61% and 84%, respectively), while increasing flexural strength by 16-38% in all resin families; neat epoxy with γ-APS also showed substantial strengthening. TGA indicated a higher onset of degradation and lower mass loss; SEM showed more cohesive fracture, consistent with siloxane anchoring to silicates and amine-epoxy or thiol-ene reactions. By combining particle packing optimization with targeted interfacial chemistry at moderate processing temperatures, the approach confirms the goals of agglomerated rock, such as improved qualities while mitigating the costs and environmental impacts associated with conventional designs that require higher resin percentages.
Keywords: Artificial rock; Coupling agents; Epoxy resin; Polyester resin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- ABIROCHAS. Brazilian Association of the Ornamental Rock Industry. Available: https://abirochas.com.br/ (in Portuguese).
-
- CENTROROCHAS. Brazilian Association of Natural Rocks. (2025). Available: https://centrorochas.org.br/en/ (in Portuguese).
-
- Silva, F. S., Ribeiro, C. E. G. & Rodriguez, R. J. S. Physical and mechanical characterization of artificial stone with marble calcite waste and epoxy resin. Mater. Res.2110.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0377 (2017).
-
- Bagherpor, Z., Nazari, S., Bagherzadeh, P. & Fazlavi, A. Description and effective parameters determination of the production process of fine-grained artificial stone from waste silica. SN Appl. Sci.1, 1458. 10.1007/s42452-019-1491-3 (2019).
-
- Srinivasan, D., Ramachandran, S., Kannadasan, K., Muthukaruppan, A. & Ismail, A. A. M. Production of engineered stone from waste foundry sand using epoxy-phenalkamine binder. Constr. Build. Mater.419, 135464. 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2024.135464 (2024).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

