Pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional DAHANCA cohort study
- PMID: 40976915
- PMCID: PMC12476047
- DOI: 10.2340/1651-226X.2025.44327
Pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional DAHANCA cohort study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Pembrolizumab is frequently used for recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (rmHNSCC) as first-line treatment. This study evaluates real-world effectiveness in a Danish and United Kingdom (UK) cohort. Patient/material and methods: Patients with confirmed rmHNSCC treated with pembrolizumab (2020-2024) as first-line palliative treatment were included consecutively. Data were collected from patient files at four Danish head and neck cancer centres (discovery cohort) and the Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust (comparison cohort). Primary endpoints were overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS).
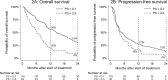
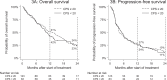
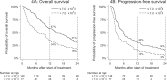
Results: In the discovery cohort (n = 228), a median OS of 10 months (95% [confidence interval [CI]: 10-12) and median PFS of 4 months (95% CI: 4-6) were found. Primary endpoints did not differ significantly between the discovery and comparison cohort. Baseline World Health Organization performance status appeared to negatively impact endpoints (hazard ratio: 1.4 [95% CI: 1.0-2.0]).
Interpretation: In this real-world multi-centre study, pembrolizumab demonstrated efficacy equivalent to the registration studies in two independent cohorts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C, Dinis J, Licitra L, Ahn MJ, et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2019;393(10167):156–67. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31999-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kenilworth NJ. FDA approves Merck’s Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for use at an additional recommended dose of 400 mg every six weeks for all approved adult indications [Internet]. [cited 2025 Jan 21]. Available from: https://www.drugs.com/newdrugs/fda-approves-merck-s-keytruda-pembrolizum...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

