CD40L and IL-4 suppress NK cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity through the HLA-E:NKG2A axis
- PMID: 40977848
- PMCID: PMC12448733
- DOI: 10.1093/immadv/ltaf029
CD40L and IL-4 suppress NK cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity through the HLA-E:NKG2A axis
Abstract
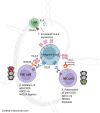
Background: Anti-CD20 antibodies are first-line treatments for B cell malignancies. Natural killer (NK) cells are important mediators of anti-CD20 antibody efficacy in humans through antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). In B cell malignancies, the lymph nodes are a critical site of pathology and the T cell-derived signals CD40L and IL-4 within the lymph node microenvironment can mediate tumour proliferation, survival and resistance to pro-apoptotic therapy. CD40L and IL-4 have recently been shown to inhibit NK cell activation against chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) cells via the HLA-E:NKG2A immune checkpoint axis. However, the effect of these signals on NK cell-mediated ADCC of malignant B cells is unclear.
Methods: Using a combination of clinical samples, murine models, flow cytometry, immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, ELISA, bioinformatics and functional assays, we examined the impact of lymph node-mimicking conditions on NK cell-mediated ADCC against malignant B cells. Exogenous CD40L and IL-4 were used to mimic T-B cell interactions in 2D malignant B cell cultures, in addition to a 3D spheroid model of T cell-dependent CLL proliferation.
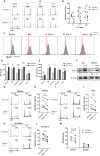
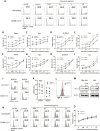
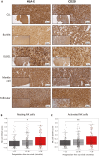
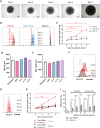
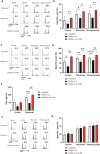
Results: CD40L and IL-4 increased HLA-E expression on the surface of primary CLL cells and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) cell lines, and this decreased NK cell-mediated ADCC via ligation of the inhibitory receptor NKG2A. High HLA-E surface expression was observed in lymph node FFPE sections of CLL and NHL patients and in a 3D ex vivo lymph node-mimicking model of CLL. NKG2A blockade potentiated NK cell-mediated ADCC against malignant B cells treated with CD40L and IL-4 and improved anti-CD20 antibody therapy in a murine model of B cell lymphoma.
Conclusion: These results reveal a novel mechanism of resistance to anti-CD20 therapy in B cell malignancies and demonstrate that the combination of anti-NKG2A with anti-CD20 could improve the treatment of patients with CLL or NHL.
Keywords: ADCC; HLA-E; NK cells; NKG2A; lymph nodes; monalizumab; rituximab.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.B and S.I.K. have applied for a patent for peptidemediated NK cell activation. M.D.B. has received research funding from Karyopharm Therapeutics. A.R. receives institutional support for grants and patents from BioInvent International and acts as a consultant for a number of biotech companies. MSC is a retained consultant for BioInvent International and has performed educational and advisory roles for Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Baxalta, Merck KGaA, Surrozen, Hanall, and GLG. He has received research funding from BioInvent International, Roche, Gilead, iTeos, Surrozen, UCB, and GSK. F.F. has received research support from Abbvie and has performed consultancies or educational activities for AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Janssen-Cilag, BC-Platform, and Beigene. No conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Cragg MS, Morgan SM, Chan HTC. et al. Complement-mediated lysis by anti-CD20 mAb correlates with segregation into lipid rafts. Blood. 2003;101:1045–52. https://doi.org/ 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1761 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mössner E, Brünker P, Moser S. et al. Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell–mediated B-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2010;115:4393–402. https://doi.org/ 10.1182/blood-2009-06-225979 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huntington ND, Cursons J, Rautela J.. The cancer–natural killer cell immunity cycle. Nat Rev Cancer 2020;20:437–54. https://doi.org/ 10.1038/s41568-020-0272-z. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41568-020-0272-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huo Z, Chen F, Zhao J. et al. Prognostic impact of absolute peripheral blood NK cell count after four cycles of R-CHOP-like regimen treatment in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clin Exp Med 2023;23:4665–72. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s10238-023-01249-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klanova M, Oestergaard MZ, Trneny M. et al. Prognostic impact of natural killer cell count in follicular lymphoma and diffuse large b-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:4634–43. https://doi.org/ 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-3270 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
