Manipulating the delivery and immunogenicity of DNA vaccines through the addition of CB[8] to cationic polymers
- PMID: 40978528
- PMCID: PMC12447565
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102585
Manipulating the delivery and immunogenicity of DNA vaccines through the addition of CB[8] to cationic polymers
Abstract
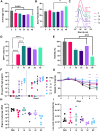
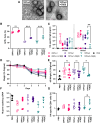
Challenges with vaccine reactogenicity, stability, and access have highlighted the need to develop alternative strategies for formulation and delivery. We explored the incorporation of cucurbit[n]urils (CBs), as supramolecular "hosts," into nucleic acid-polymer polyplexes. CBs are small, non-toxic, barrel-shaped molecules that transiently crosslink polymers containing supramolecular "guests," thereby increasing molecular weight (MW) of the complex, a correlate of transfection efficiency. We tested whether the supramolecular interactions of CB[8] impact polyplex function. We generated a library of different CB[8] polyplexes using plasmid DNA (pDNA), varying N/P (the ratio of polymer to plasmid), the length, and guest (phenylalanine [Phe]) group frequency of the polyethylenimine (PEI) polymer backbone. We found that N/P 32 and the 20Phe1 (20kDa PEI with 1 mol% Phe) gave optimal gene expression and that incorporating CB[8] in polyplex formulations improved gene expression, both in vitro and in vivo. Despite increases in gene expression, inclusion of CB[8] in formulations with higher guest-binding capacity led to decreased immunogenicity, possibly as a result of dampened innate immune responses. Our data show that CB[8] polyplexes increase gene delivery and expression but alter inflammatory responses. These findings highlight that rational design of the CB[8] polymer system can enable nucleic acid delivery for both vaccine and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: DNA vaccine; MT: Delivery Strategies; cucurbituril; nucleic acid delivery; polymeric nanoparticles; polyplex.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
B.T.C., A.M.H., and R.C. are employees and have an equity interest in Aqdot (Cambridge, UK).
Figures



References
-
- Pardi N., Parkhouse K., Kirkpatrick E., McMahon M., Zost S.J., Mui B.L., Tam Y.K., Karikó K., Barbosa C.J., Madden T.D., et al. Nucleoside-modified mRNA immunization elicits influenza virus hemagglutinin stalk-specific antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2018;9 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05482-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McKay P.F., Hu K., Blakney A.K., Samnuan K., Brown J.C., Penn R., Zhou J., Bouton C.R., Rogers P., Polra K., et al. Self-amplifying RNA SARS-CoV-2 lipid nanoparticle vaccine candidate induces high neutralizing antibody titers in mice. Nat. Commun. 2020;11 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17409-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

