Current and Future Applications of AI in EMS Training: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 40979032
- PMCID: PMC12445063
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.90469
Current and Future Applications of AI in EMS Training: A Scoping Review
Abstract
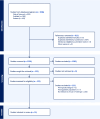
Over the last 15 years, AI has been increasingly utilized in healthcare education. In EMS, AI is being used to train providers for their high-stress, dynamic environments. This scoping review examines current and future applications of AI in EMS training, with a focus on simulation, interventions, personalized learning, and disaster preparedness. A librarian-assisted literature search was conducted across PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science using terms related to EMS, AI, and education. Articles published between January 1, 2010 and March 16, 2025 were screened and selected based on relevance. Studies were reviewed by title, abstract, and full text, followed by data extraction. Currently, AI has been integrated to enhance EMS training through advanced simulation, procedure training, development of personalized learning materials, and disaster response. These improvements are made possible by utilizing different types of AI tools such as machine learning, natural language processing, and large language models. AI tools showed improvements in realism, diagnostic accuracy, feedback delivery, and learner adaptability. It is actively transforming EMS training by strengthening provider readiness, clinical judgment, and educational outcomes. With continued research and development, its integration could further enhance training effectiveness. Ethical and implementation challenges remain, but increased education and awareness can help ensure that AI is used to positively affect patient care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; disaster medicine; emergency medical services; ems education; large language models; machine learning; personalized learning; prehospital care; simulation training; virtual reality.
Copyright © 2025, Pasquariello et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- A systematic literature review of artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector: benefits, challenges, methodologies, and functionalities. Ali O, Abdelbaki W, Shrestha A, Elbasi E, Alryalat MAA, Dwivedi YK. J Innov. 2023;8:100333.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources