A New Prognostic Score Based on Cell-Mediated Immunity for Cytomegalovirus Infection After Transplantation
- PMID: 40980655
- PMCID: PMC12446942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.06.056
A New Prognostic Score Based on Cell-Mediated Immunity for Cytomegalovirus Infection After Transplantation
Abstract
Introduction: The interferon gamma (IFN-γ) enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot is a highly sensitive immune assay that enables the assessment of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-specific cell-mediated immunity (CMI) and can identify at-risk transplant patients of CMV infection; however, its clinical implementation remains elusive.
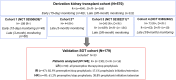
Methods: We developed a novel CMV-CMI risk-score based on the standardized T-SPOT.CMV assay against 2 CMV antigens (immediate-early protein 1 [IE-1] and 65 kDa phosphoprotein [pp65]), a biomarker predicting CMV infection, both high viral replication, and disease by performing a pooled analysis of 570 kidney transplants participating in different clinical trials and subsequently validating it in 146 consecutives solid organ transplants (SOT) in an interventional trial. By incorporating clinical variables into the CMV-CMI risk-score, we built an integrative prognostic system quantifying the risk of CMV infection (CMV-PrognosTIC score) using elastic net penalized regression analysis.
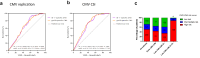
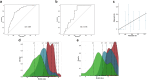
Results: In the pooled derivation cohort, whereas specific IE-1/pp65-specific CMV-CMI frequencies independently correlated with high risk of CMV infection (areas under the curve [AUCs]: 0.694, P < 0.0001; 0.719, P < 0.0001, respectively), by combining both responses, 3 CMV-CMI risk-scores appeared, accurately discriminating low-risk (LR) from intermediate-risk (IR) and high-risk (HR) patients (98.7% negative predictive value [NPV], 97.2% sensitivity). Its prospective implementation guiding decision-making in an independent SOT cohort confirmed the very high NPV and sensitivity identifying LR patients. By integrating type of preventive therapy, patient age, and donor (D) and recipient (R) CMV-serostatus to the CMV-CMI risk-score, we generated a global risk-prognostic model showing accurate discrimination and calibration in both derivation (AUC: 0.807) and validation cohorts (AUC: 0.719).
Conclusion: We developed a robust CMV-PrognosTIC score to quantify the risk of CMV infection in SOT, which may be readily implemented in clinical transplantation to personalize CMV preventive therapies.
Keywords: CMV infection; cell-mediated immunity; monitoring; solid organ transplantation.
© 2025 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

