Improvement in global longitudinal strain following plasma cell-directed therapy is associated with long-term survival among patients with AL amyloidosis
- PMID: 40980714
- PMCID: PMC12449083
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oeaf104
Improvement in global longitudinal strain following plasma cell-directed therapy is associated with long-term survival among patients with AL amyloidosis
Abstract
Aims: Cardiac impairment in AL amyloidosis is the major determinant of survival. Treatment goals include reducing circulating light chains to improve organ function. Global longitudinal strain (GLS) is an independent predictor of survival and useful for assessing cardiac function before and after therapy. This study aimed to describe GLS change from baseline to one year post-treatment, identify factors associated with GLS improvement (GLS+), and evaluate its prognostic significance.
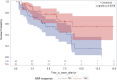
Methods and results: Ninety-seven patients with AL amyloidosis and cardiac stage II/III disease who underwent echocardiogram and haematologic evaluation at baseline and one year were included. GLS+ was defined as a 2.0%-point increase. A cardiac or B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP+) response was defined as a 30% reduction from baseline. Overall survival was measured from baseline echocardiogram to death. Of 97 patients, 62% had Stage II, 29% Stage IIIa, and 9% Stage IIIb disease. Baseline median left ventricular ejection fraction, GLS, and septal thickness were 65%, -14.9%, and 1.3 cm, respectively. GLS+ was observed in 36% of patients and BNP+ in 51%. Median overall survival was 113.4 months. The hazard ratio for survival was 0.42 in the GLS+ group and 0.46 in the BNP+ group, after adjusting for haematologic response.
Conclusion: GLS improvement post-treatment confers a significant survival benefit. This study supports GLS as an important marker for risk stratification and cardiac response.
Keywords: AL amyloidosis; Cardiomyopathy; Echocardiography; Global longitudinal strain; Prognosis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: A.F.Y.: consultancy for Genentech and Avacta; grant support from Merck. H.L.: consultancy for Pfizer, Prothena, Legend Biotech USA, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceuticals; research funding from Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceuticals. M.S.M.: researcher for NIH R01HL139671 and R01AG081582-01, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, BridgeBio (formerly Eidos Therapeutics), Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, and Prothena Biosciences; and as a consultant or advisor for Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Attralus, BridgeBio (formerly Eidos Therapeutics), Intellia Therapeutics, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. D.L.: consultant for Myocardial Solutions, AstraZeneca, Clementia, and Intellia; speaker for BridgeBio. J.E.L.: DMSB for Caelum Biosciences; research support from Johnson and Johnson; speaking fees from GE Healthcare and Philips Medical. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Muchtar E, Gertz MA, Kumar SK, Lacy MQ, Dingli D, Buadi FK, Grogan M, Hayman SR, Kapoor P, Leung N, Fonder A, Hobbs M, Hwa YL, Gonsalves W, Warsame R, Kourelis TV, Russell S, Lust JA, Lin Y, Go RS, Zeldenrust S, Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A. Improved outcomes for newly diagnosed AL amyloidosis between 2000 and 2014: cracking the glass ceiling of early death. Blood 2017;129:2111–2119. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Palladini G, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kumar S, Wechalekar A, Hawkins PN, Schönland S, Hegenbart U, Comenzo R, Kastritis E, Dimopoulos MA, Jaccard A, Klersy C, Merlini G. New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: impact on survival outcomes. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:4541–4549. - PubMed
-
- Pun SC, Landau HJ, Riedel ER, Jordan J, Yu AF, Hassoun H, Chen CL, Steingart RM, Liu JE. Prognostic and added value of two-dimensional global longitudinal strain for prediction of survival in patients with light chain amyloidosis undergoing autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2018;31:64–70. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buss SJ, Emami M, Mereles D, Korosoglou G, Kristen AV, Voss A, Schellberg D, Zugck C, Galuschky C, Giannitsis E, Hegenbart U, Ho AD, Katus HA, Schonland SO, Hardt SE. Longitudinal left ventricular function for prediction of survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis: incremental value compared with clinical and biochemical markers. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012;60:1067–1076. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

