Bacillus Pectinases as Key Biocatalysts for a Circular Bioeconomy: From Green Extraction to Process Optimization and Industrial Scale-Up
- PMID: 40981378
- PMCID: PMC12452564
- DOI: 10.3390/biotech14030074
Bacillus Pectinases as Key Biocatalysts for a Circular Bioeconomy: From Green Extraction to Process Optimization and Industrial Scale-Up
Abstract
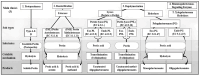
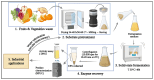
Pectins are high-value plant cell-wall polysaccharides with extensive applications in the food, pharmaceutical, textile, paper, and environmental sectors. Traditional extraction and processing methodologies rely heavily on harsh acids, high temperatures, and non-renewable solvents, generating substantial environmental and economic costs. This review consolidates recent advances across the entire Bacillus-pectinase value chain, from green pectin extraction and upstream substrate characterization, through process and statistical optimization of enzyme production, to industrial biocatalysis applications. We propose a practical roadmap for developing high-efficiency, low-environmental-footprint enzyme systems that support circular bioeconomy objectives. Critical evaluation of optimization strategies, including submerged versus solid-state fermentation, response surface methodology, artificial neural networks, and design of experiments, is supported by comparative data on strain performance, fermentation parameters, and industrial titers. Sector-specific case studies demonstrate the efficacy of Bacillus pectinases in fruit-juice clarification, textile bio-scouring, paper bio-bleaching, bio-based detergents, coffee and tea processing, oil extraction, animal feed enhancement, wastewater treatment, and plant-virus purification. Remaining challenges, including enzyme stability in complex matrices, techno-economic scale-up, and structure-guided protein engineering, are identified. Future directions are charted toward CRISPR-driven enzyme design and fully integrated circular-economy bioprocessing platforms.
Keywords: Bacillus spp.; agro-industrial waste valorization; circular bioeconomy; industrial biocatalysis; pectin; pectinolytic enzymes; solid-state fermentation; statistical enzyme optimization; thermostable enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Morone P., D’Amato D., Befort N., Yilan G. The Circular Bioeconomy: Theories and Tools for Economists and Sustainability Scientists. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2023. - DOI
-
- Gallego L., Harvey K., Pevida M., García-Consuegra L., García-Suárez O., Meana Á., Alvarez-Viejo M., Junquera L. From Waste to Innovation: A Circular Economy Approach for Tissue Engineering by Transforming Human Bone Waste into Novel Collagen Membranes. Biomolecules. 2025;15:132. doi: 10.3390/biom15010132. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bijesh K., Sebastian D. Review on bacterial production of alkaline pectinase with special emphasis on Bacillus species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2018;11:18–30. doi: 10.21786/bbrc/11.1/4. - DOI
-
- Rehman H.U. Applications of Pectinolytic Enzymes in Process Industries. In: Ahmed M., editor. Utilization of Pectin in the Food and Drug Industries. IntechOpen; Rijeka, Croatia: 2023. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
