Impact of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide on health-related quality of life and economic outcomes in HIV care: Substudy of the BIC-NOW clinical trial
- PMID: 40982450
- PMCID: PMC12453196
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323167
Impact of bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide on health-related quality of life and economic outcomes in HIV care: Substudy of the BIC-NOW clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The BICNOW clinical trial evaluated the effectiveness, safety, satisfaction, adherence to treatment, and retention in the system of a rapid initiation strategy with bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (BIC/FTC/TAF) in naïve HIV-infected individuals. It also assessed the burden of this infection on individuals and healthcare systems using various instruments, participant questionnaires, and pharmacoeconomic evaluations of this antiretroviral therapy (ART). This substudy focused on changes in the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of participants and on the economic impact of this rapid initiation strategy.
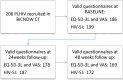
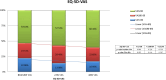
Methods and findings: Patients were recruited for this phase IV, multicenter, open, single-branch clinical trial with 48-week follow-up between November 2020 and July 2022. HRQoL data were gathered using EQ-5D-3L and dichotomized HIV-SI questionnaires. In the cost-utility pharmacoeconomic analysis, data in the literature were used for comparators. The 208 participants had a mean age of 34 (27-44) years, 87·5% were male, 42·9% had completed higher education, and 67·1% were employed. The mean EQ-5D questionnaire score was significantly increased at 48 weeks versus baseline (0·940 ± 0·117 vs. 0·959 ± 0·083, p = 0·012), and the utility value in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) was 0·877 ± 0·093. There was a significant improvement in the "usual activities" dimension (10·8 vs 4·1% p = 0·036). The Moses extreme reaction test showed a significant difference in all dimensions between participants in AIDS versus non-AIDS stage (p < 0·001). HIV-SI results revealed a significantly smaller percentage of participants with bothersome symptoms at 48 weeks (75·4 vs. 62·2%, p = 0·035). The pharmacoeconomic study indicated a value of €6,550·21/QALY gained with this ART.
Conclusions: BIC/FTC/TAF is an appropriate rapid initiation strategy in naïve PLHIV that improves their quality of life. It is pharmacoeconomically feasible and offers superior long-term health outcomes in comparison to other approaches. (NCT06177574).
Copyright: © 2025 Sequera-Arquelladas et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
CHT has received honararia for consulting or speaking at educational events from Janssen, Gilead, MSD and ViiV.
Figures
References
-
- Safreed-Harmon K, Fuster-RuizdeApodaca MJ, Pastor de la Cal M, Lazarus JV. Problems undermining the health-related quality of life of people living with HIV in Spain: a qualitative study to inform the development of a novel clinic screening tool. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2022;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-01978-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EACS Guidelines 2023. In: EACS Guidelines [Internet]. 2023. [cited 21 Apr 2024]. Available: https://eacs.sanfordguide.com
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical