Allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation in advanced systemic mastocytosis in the new era: A CIBMTR study
- PMID: 40983528
- PMCID: PMC12519450
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.70154
Allogeneic haematopoietic cell transplantation in advanced systemic mastocytosis in the new era: A CIBMTR study
Abstract
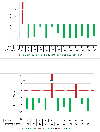
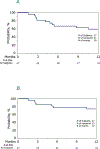
We investigated the outcomes of patients with advanced systemic mastocytosis (AdvSM) undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic cell therapy (alloHCT) in the US. Twenty-seven adult (median age, 58 years) patients with AdvSM received alloHCT from 2014 to 2021. Most patients were white (93%), male (63%) and had systemic mastocytosis (SM) with associated haematological neoplasm (SM-AHN, 70%), received peripheral blood grafts (89%) and non-myeloablative regimens. KIT mutation was detected in 14 of the reported 16 patients (87.5%). Post-transplantation cyclophosphamide (PTCy) was used in approximately 50% of the cohort. Approximately 1 year after alloHCT, median bone marrow mast cell burden decreased from 15% pre-alloHCT to 1.5% (range 0-8) at 1 year post-alloHCT. The median serum tryptase decreased from 55 ng/mL (range 3-400 ng/mL) pre-alloHCT to 18 ng/mL (range 0-481 ng/mL) at 1 year post-alloHCT. At 1 year, progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were 59% (95% confidence interval [CI], 41%-77%) and 74% (95% CI, 56%-89%) respectively. In the subset of patients with SM-AHN, 1-year PFS and OS were 74% (52%-91%) and 79% (95% CI, 58%-94%) respectively. The cumulative incidence of relapse/progression for the entire population of patients with SM (n = 27) was 4% (95% CI, 0-14) at 100 days and 15% (95% CI, 4-31) at 1 year. For the subset of patients with AHN, the cumulative incidence was 11% (95% CI, 1-28) at 100 days and 21% (95% CI, 6-42) at 1 year. Relapse/progression was the cause of death in six of 12 patients (5 died of AHN and 1 died of SM progression). Eighteen and nine patients received a KIT inhibitor before alloHCT and after alloHCT respectively. In addition, six patients received a KIT inhibitor for the treatment of relapse/progression of SM after alloHCT. Although it is difficult to delineate the exact effect of alloHCT and KIT inhibitors because of the size of the study in this era, the use of alloHCT and KIT inhibitors pre- and post- alloHCT is increasing. In the near future, larger studies are required to provide further insights into this subject.
Keywords: allogeneic; bone marrow transplantation; mast cells; systemic mastocytosis; tryptase.
© 2025 British Society for Haematology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest:
• Munzer Agha:No COI
• Arpita Gandhi:
○ CareDx - AdBoard
OncLive- Honorarium
MJH Life Sciences - Honorarium
OrcaBio - Research
• Cem Akin: has consultancy agreements with Blueprint, Cogent, Allakos, and Novartis; and receives research support from Blueprint and Cogent.
• Hassan Alkhateeb: No COI
• Alexander Baek: No COI
• Linda Burns: No COI
• Saurabh Chhabra: honoraria from Sanofi, Ascentage Pharma, Sobi, Legend Biotech, and institutional research funding from Johnson & Johnson, Takeda, C4 Therapeutics, Abbvie, Ascentage Pharma, AstraZeneca.
• Aleander Coltoff: Honoria Sobi: Speaker’s Bureau, Advisory Board, PharmaEssentia: Advisory Board
• Daniel DeAngelo. received honoraria from Amgen, Autolus, Agios, Blueprint Pharmaceuticals, Forty Seven, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Kite Pharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Shire, and Takeda, and research support from AbbVie, GlycoMimetics, Novartis, and Blueprint Medicines
• Marcus De Lima: consulting or advisory role at BMS, Autolus, and Pfizer; research funding from Miltenyi and Priothera; and he is on the data monitoring committee at AbbVie and Novartis
• Jason Gotlib received research grant (funds for administration of clinical trials) from Blueprint Medicines, Cogent Biosciences, Incyte, BMS, Merck, and Protagonist Therapeutics, is on the advisory board of and received honoraria from Blueprint Medicines and Cogent Biosciences, and got reimbursement of travel expenses from Blueprint Medicines.
• Michael Grunwald:
a) Consulting fees – Amgen, Aptitude Health, Astellas, Blueprint Medicines, Cardinal Health, Cogent Biosciences, Daiichi Sankyo, Disc Medicine, Incyte, Janssen, Karius, OncLive, Premier, Sanofi, Servier, Sobi, Takeda.
b) Research support – Ajax, Incyte, Janssen.
c) Stock ownership – Medtronic.
• Mehdi Hamdani:
Research Support/Funding: ADC Therapeutics; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals.
Consultancy: Genmab, CRISPR, Allovir, Caribou, Autolus, Forte Biosciences, Byondis, Kite, Daiichi Sankyo
Speaker’s Bureau: AstraZeneca, ADC Therapeutics, BeiGene, Kite, Sobi
DMC: Myeloid Therapeutics), CRISPR
• Vincent Ho:Grants from PCORI during the conduct of the study; consulting/advisory fees from Alexion, Sanofi, and Omeros; and research support from Jazz, AlloVir, and Immunogen outside the submitted work.
• Mark Juckett: No COI
• Adetola Kassim: No COI
• Guido Marcucci: stock and other ownership interests in Ostentus Therapeutics, Inc.
• Lohith Gowda: No COI
• Michael Linden; No COI
• Joseph McGuirk: Consultancy: BMS, Kite, Novartis, Allo Vir, Envision, Autolus, NEKTAR therapeutics, CRISPR therapeutics, Caribou bio, Sana technologies, Legend biotech.
• Aaron Logan: consulting or advisory role for Amgen, Pfizer, Sanofi, Kite, and Takeda; research funding from Astellas Pharma, Pharmacyclics, Kite/Gilead, Kadmon, Amgen, Autolus, Talaris; and travel, accommodations, and expenses from Amgen
• Felix Mensah:No COI
• Taiga Nishohiri:clinical trial support from Novartis to the institution and clinical trial support (drug only supply) by Karyopharm to the institution.
• Kalyan V Nadiminti: consultancy/advisory board, Sobi pharmaceuticals
• Betul Oran: No COI
• Andrew Peterson: No COI
• Jeremy Pantin: speaker’s bureau work for Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb and Omeros Corporation and honoraria and consultancy from Legend Biotech and Novartis Pharmaceuticals
• Vinod Pullarkat: advisory board fees/consultancy/speaker’s bureau from AbbVie, Genentech, Pfizer, Jazz, Novartis, Rigel, Sobi, Sanofi, and Amgen
• Wael Saber: No COI
• Andrew Trunk: No COI
• Joseph Uberti: No COI
• Celalettin Ustun: Honoria from Blueprint for speaker bureau
Stock of Cogent Bioscience, Actinium, Iovance
• Peter Valent:
Research grant: AOP Orpha:
2. Consultant honoraria (advisory board and/or speaker): Novartis, Blueprint, Cogent, Pfizer, AOP Orphan, Stemline, Daiichi Sankyo, Amgen, PentaBase, Delbert.
• Adam Y Lin: No COI
• Mei-Jie Zhang: No COI
Figures

References
-
- Lim KH, Tefferi A, Lasho TL, et al. Systemic mastocytosis in 342 consecutive adults: survival studies and prognostic factors. Blood. 2009;113(23):5727–5736. - PubMed
-
- Valent P, Hartmann K, Hoermann G, et al. Harmonization of Diagnostic Criteria in Mastocytosis for Use in Clinical Practice: WHO vs ICC vs AIM/ECNM. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024;12(12):3250–3260 e3255. - PubMed
-
- Valent P, Sotlar K, Horny HP, Arock M, Akin C. World Health Organization Classification and Diagnosis of Mastocytosis: Update 2023 and Future Perspectives. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2023;43(4):627–649. - PubMed
-
- Valent P, Akin C, Arock M, et al. Antibody-Based and Cell Therapies for Advanced Mastocytosis: Established and Novel Concepts. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

