Assessment of environmental risk factors for blastomycosis during a large outbreak at a Michigan paper mill
- PMID: 40986553
- PMCID: PMC12456783
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0332398
Assessment of environmental risk factors for blastomycosis during a large outbreak at a Michigan paper mill
Abstract
Background: Blastomycosis is a rare, potentially fatal fungal infection caused by inhalation of Blastomyces spores, typically acquired outdoors in the midwestern and eastern United States. In 2023, the largest recorded U.S. blastomycosis outbreak occurred among workers at a paper mill in Michigan's Upper Peninsula. Few data exist on occupational risk factors or indoor exposure to Blastomyces, limiting prevention efforts.
Objectives: We assessed workplace environments and conditions associated with blastomycosis risk through a cross-sectional medical survey and environmental sampling.
Methods: During April 22-28, 2023, we conducted a voluntary medical survey, including a work and health questionnaire and urine antigen testing, for 603 workers out of approximately 1,000 at the mill. We compared worker characteristics, work locations, and environmental exposures by blastomycosis case status and modeled disease risk using Poisson regression. We tested 533 environmental samples of outdoor soil, indoor surface dust, and raw materials for Blastomyces using polymerase chain reaction and culture-based methods.
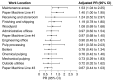
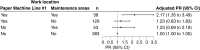
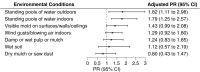
Results: Twenty percent of workers were classified as blastomycosis cases based on positive urine antigen testing during the survey, self-reported provider diagnoses, or confirmed or probable case status reported by state or local health departments. Prevalence was highest among workers in paper machine line #1 (27%) and maintenance areas (25%). Adjusted analyses indicated a 40% [Prevalence Ratio (PR): 1.40; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.00, 1.95] and 53% (PR: 1.53; 95% CI: 1.04, 2.25) higher risk for workers in these locations, respectively, compared to workers working elsewhere. Working in both locations doubled blastomycosis risk. Daily exposure to indoor pooling water was associated with a nearly two-fold higher prevalence of blastomycosis (PR: 1.79; 95% CI: 1.25, 2.57). All indoor and outdoor environmental samples were negative for Blastomyces.
Discussion: Blastomycosis was associated with specific indoor work locations and environmental conditions, suggesting the potential for occupational exposure to Blastomyces in indoor industrial settings. These findings may guide future outbreak investigations and occupational prevention strategies.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Harvey RR, O’Connor AW, Park JH, Shi D, Callaway PC, Liang X, et al. Outbreak of blastomycosis among paper mill workers — Michigan, November 2022–May 2023. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Rep. 2025;73(51–52).
-
- CDC USD o H a HS. Data and statistics on blastomycosis. 2024 [Accessed 2025 April 6]. https://www.cdc.gov/blastomycosis/data-research/statistics/index.html
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

