Cholesterol metabolic reprogramming mediates microglia-induced chronic neuroinflammation and hinders neurorestoration following stroke
- PMID: 40987840
- PMCID: PMC12552130
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-025-01379-7
Cholesterol metabolic reprogramming mediates microglia-induced chronic neuroinflammation and hinders neurorestoration following stroke
Abstract
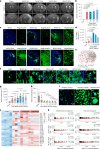
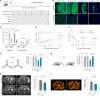
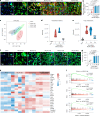
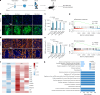
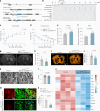
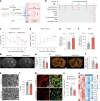
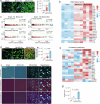
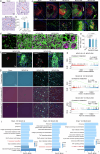
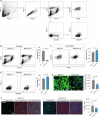
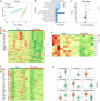
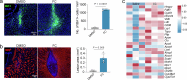
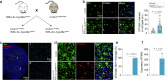
Chronic neuroinflammation is a major obstacle to post-stroke recovery, yet the underlying mechanisms, particularly the link between prolonged microglial activation and cholesterol metabolism, are not fully known. Here we show that ischaemic injury induces persistent microglial activation that perpetuates chronic inflammation, leading to microglial cholesterol accumulation and metabolic reprogramming. Using single-cell RNA sequencing, we identified distinct stroke-associated foamy microglia clusters characterized by extensive reprogramming of cholesterol metabolism. Furthermore, direct intracerebral free cholesterol or cholesterol crystal infusion recapitulated sustained microglial activation, directly linking aberrant cholesterol metabolism to prolonged neuroinflammatory responses. Therapeutically, we demonstrate that reducing microglial cholesterol overload through genetic or pharmacological activation of CYP46A1 in male mice promotes white matter repair and functional recovery. These findings highlight microglial cholesterol metabolism as a key driver of post-stroke inflammation, offering therapeutic strategies targeting cholesterol metabolism to mitigate long-term brain damage and promote neurorestoration, potentially improving stroke-related disability outcomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hacke, W. et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med.359, 1317–1329 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Pappata, S. et al. Thalamic microglial activation in ischemic stroke detected in vivo by PET and [11C]PK1195. Neurology55, 1052–1054 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Gerhard, A., Schwarz, J., Myers, R., Wise, R. & Banati, R. B. Evolution of microglial activation in patients after ischemic stroke: a [11C](R)-PK11195 PET study. Neuroimage24, 591–595 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Shi, K. et al. Global brain inflammation in stroke. Lancet Neurol.18, 1058–1066 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

