Predicting prognosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis with kidney involvement
- PMID: 40989994
- PMCID: PMC12451443
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfaf268
Predicting prognosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis with kidney involvement
Abstract
Background: The ANCA Renal Risk Score was updated in 2023 to the ANCA Kidney Risk Score (AKRiS) to improve clinicopathological prognostication in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) and kidney involvement. Our study aimed to assess whether incorporating recently identified predictors of kidney survival in AAV could further refine the prognostic accuracy of AKRiS in our multicentric cohort.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all incident AAV with kidney biopsy from 2005 to 2020. Cox regression analysis examined factors [AKRiS, dialysis within 4 weeks, urine protein-creatinine ratio (UPCR) and hematuria at baseline, C3 deposits, renal arteritis on biopsy, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), UPCR and hematuria after induction] associated with kidney failure. These factors in combination with AKRiS were analyzed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) for prediction of kidney failure.
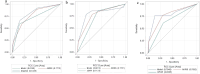
Results: The cohort included 115 patients (age 64 years, 55% male, 57% myeloperoxidase-ANCA, baseline creatinine 3.6 mg/dL, eGFR 16 mL/min/1.73 m2), with 34 (30%) dialysed within 4 weeks. During a median 6.4-year follow-up, 39 (34%) patients progressed to kidney failure, and 13 (11%) died. Cox analysis identified AKRiS, dialysis within 4 weeks, C3 deposits, renal arteritis on biopsy, lower eGFR after induction and higher UPCR after induction as unadjusted risk factors for kidney failure. After adjusting for AKRiS, dialysis within 4 weeks [hazard ratio (HR) 6.20 (95% confidence interval 2.76 to 13.95), P ≤ .001], eGFR after induction [HR 0.94 (0.89 to 0.99), P = .03] and UPCR after induction [HR 1.62 (1.02 to 2.58), P = .04] remained significantly associated with kidney outcome. The AUROC for kidney failure prediction was 0.77 for AKRiS, increasing to 0.82, 0.80 and 0.79 when adding dialysis within 4 weeks, eGFR and UPCR after induction, respectively.
Conclusion: Dialysis within 4 weeks, eGFR after induction and UPCR after induction are able to predict long-term kidney outcome in AAV patients. Adjusting AKRiS for these variables modestly enhances its predictive power. We propose using them as placeholder endpoints for kidney failure in future studies.
Keywords: AKRiS; ANCA Renal Risk Score; pauci-immune necrotizing glomerulonephritis.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

