Identification of a KRT9 gene variant and preimplantation genetic diagnosis in a Chinese family with KRT9-palmoplantar epidermal differentiation disorder
- PMID: 40993822
- PMCID: PMC12462274
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-025-00552-y
Identification of a KRT9 gene variant and preimplantation genetic diagnosis in a Chinese family with KRT9-palmoplantar epidermal differentiation disorder
Abstract
Objective: To investigate a Chinese family with epidermolysis bullosa palmoplantar keratosis, analyze the mutation loci in this family lineage, and perform preimplantation genetic testing using assisted reproductive technology to enable affected members of this Chinese family to have unaffected offspring.
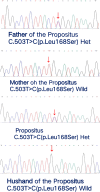
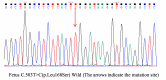
Methods: Clinical information and blood samples were collected from all affected family members to extract genomic DNA. We detected a mutation site in the KRT9 gene through whole-exome sequencing, then verified this family line's Keratin-9 gene variant locus using Sanger sequencing. After the pathogenicity was clarified, blastocyst trophoblast cells were extracted for Preimplantation Genetic Testing for Monogenic (PGT-M)(Single Gene) Disorders using the in vitro fertilization embryo transfer technique, and suitable embryos were selected for transfer. Amniocentesis was performed to extract fetal exfoliated cells for prenatal diagnosis at 18 weeks of fetal development.
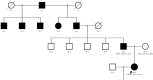
Results: A heterozygous mutation c.503T > C (p. Leu168Ser), which results in the substitution of a leucine for a serine (p. Leu168Ser), was detected in the KRT9 gene in the proband and his father, which is located in the highly conserved helix 1 A region of Keratin 9, resulting in an abnormal function of the intermediate filamentous proteins expressed by Keratin 9 encodes genes which are expressed in the palmo-plantar regions of the epidermis, and the patients of the family present with pronounced palmar-plantar keratoderma.
Conclusion: We identified the c.503T > C (p. Leu168Ser) missense mutation in exon 1 of the KRT9 gene as the cause of KRT9-palmoplantar epidermal differentiation disorder (KRT9-pEDD) in a Chinese family. Under the guidance of comprehensive genetic counseling, employing PGT-M, we successfully prevented the transmission of the KRT9-pEDD pathogenic variant, resulting in the birth of a healthy child.
Keywords: KRT9; Missense mutation; PGT-M; Prenatal diagnosis; Whole-exome sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University (Ethical approval number: 2023-KYL-264). Informed consent was obtained from the parents for using clinical information and sample collection involved in this study. Consent for publication: Informed Consent to publication from the participant or all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s) was obtained to publish their study as research. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Li P, Qi J, Zhong Y, Ding A, Xiao H. Proteomic profiling reveals KRT6C as a probable hereterodimer partner for KRT9: new insights into re-classifying epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma (EPPK) and a milder form of Pachyonychia congenita (PC-K6c) as a group of genetic cutaneous disorders. J Proteom. 2023;287:104971. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Valdez J, Rivera-Vega MR, Gonzalez-Huerta LM, Cazarin J, Cuevas-Covarrubias S. Analysis of the KRT9 gene in a Mexican family with epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30(3):354–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu N, Shi H, Kong X, Wu Q, Jiang M. Mutation analysis and prenatal diagnosis of keratin 9 gene in a large Chinese family with epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2014;31(1):48–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

