Incidence of Recurrent Adverse Cardiovascular Events Among Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction During the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Bangladesh: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 40994781
- PMCID: PMC12453963
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71254
Incidence of Recurrent Adverse Cardiovascular Events Among Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction During the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic in Bangladesh: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background and aims: COVID-19 is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. We investigated undiagnosed COVID-19 and its effect on recurrent adverse cardiovascular events among patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI).
Methods: We enrolled patients with either ST-segment elevation (STEMI) or non ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) presenting at the National Institute of Cardiovascular Disease, Dhaka, from June 28 to August 11, 2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were collected for SARS-CoV-2 testing by rRT-PCR at enrolment. We followed all patients from admission until February 7, 2021, before the COVID-19 vaccination in Bangladesh, to register clinical endpoints (all-cause death, new AMI, heart failure, or new revascularization). Demographic information, cardiovascular risk factors, and clinical data were registered. Incidence rate (IR) per 100 person-years follow-up was calculated for clinical endpoints. Poisson regression was employed to estimate the incidence rate ratio (IRR) for SARS-COV-2 infection, adjusting for age.
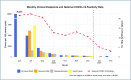
Results: We enrolled 280 patients with a mean age of 54.5 ( ± SD,11.8) years, and 78.6% were males. Of them, 12.9% had undiagnosed SARS-CoV-2 infection and were diagnosed with STEMI (n = 140, 50.0%) and NSTEMI (n = 140, 50.0%). We found that the IR per 100 person-years of all cause death was 35.2, 95% CI: 25.6 to 48.5; recurrent AMI was 18.5, 95% CI: 12.1 to 28.2; heart failure was 6.7, 95% CI: 3.3 to 13.5; and revascularization was 23.5, 95% CI: 16.1 to 34.3. Patients with COVID-19 had numerically higher IRRs for heart failure (2.40, 95% CI: 0.47 to 12.09, p = 0.290) and revascularization (1.11, 95% CI: 0.37 to 3.3, p = 0.853) compared to those without COVID-19, though these differences were not statistically significant.
Conclusion: This study provides updated data on undiagnosed cases among AMI patients during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings emphasize the need for further research to explore the impact of COVID-19 on AMI patients in resource-limited settings like Bangladesh.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Ole Fröbert reports consultancy fees from GSK and speaker's fees from Pfizer and Sanofi. Timothy C. Tan reports consultancy fees from GSK and Bayer, as well as speakers's fees from GSK, Amgen, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim and Sanofi. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

