Multiparametric MRI combined with PSA density as a noninvasive rule-out strategy in active surveillance for prostate cancer
- PMID: 40995188
- PMCID: PMC12453940
- DOI: 10.1002/bco2.70079
Multiparametric MRI combined with PSA density as a noninvasive rule-out strategy in active surveillance for prostate cancer
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic performance of multiparametric MRI (mpMRI), mpMRI combined with PSA density (PSAd) and combined biopsy (CBx) in detecting clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa) in men undergoing active surveillance, using radical prostatectomy (RP) specimens as the reference standard.
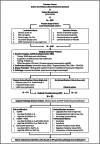
Patients and methods: In this prospective single-centre study, 91 patients with low-risk prostate cancer under active surveillance underwent mpMRI, PSAd measurement, CBx and ultimately RP. mpMRI was reported using PI-RADS v2.0, and PSAd was dichotomised at 0.12 ng/ml/cm3. Diagnostic accuracy was compared using ISUP grade ≥2 and ≥3 thresholds. Radical prostatectomy pathology served as the reference standard.
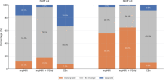
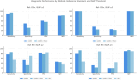
Results: For detecting ISUP ≥3 cancer, mpMRI combined with PSAd achieved the highest sensitivity (93.3%) and negative predictive value (94.4%). CBx demonstrated the highest specificity (88.2%) and overall diagnostic balance (Youden index = 0.348). mpMRI alone showed intermediate performance. Differences in classification between strategies were statistically significant (McNemar p < 0.001).
Conclusions: mpMRI combined with PSAd provides high sensitivity and negative predictive value for ruling out aggressive prostate cancer, supporting its use as a non-invasive triage tool in active surveillance. CBx remains the most specific method for histological confirmation. These strategies should be used complementarily to optimise decision-making in active surveillance protocols.
Keywords: ISUP grade; PSA density; active surveillance; combined biopsy; mpMRI; prostate cancer; radical prostatectomy.
© 2025 The Author(s). BJUI Compass published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International Company.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aerts J, Hendrickx S, Berquin C, Lumen N, Verbeke S, Villeirs G, et al. Clinical application of the prostate cancer radiological estimation of change in sequential evaluation score for reporting magnetic resonance imaging in men on active surveillance for prostate cancer. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2023;56:39–46. 10.1016/j.euros.2023.08.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed HU, Bosaily AE, Brown LC, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi‐parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): a paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet. 2017;389(10071):815–822. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
