Large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL): EHA Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up
- PMID: 40995463
- PMCID: PMC12456099
- DOI: 10.1002/hem3.70207
Large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL): EHA Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up
Abstract
Large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) accounts for about one-third of adult lymphoma cases. Diagnosis requires specialized hematopathology laboratories, with immunophenotypic analysis essential for confirming B-cell lineage and identifying variants. MYC and BCL2 rearrangements indicate a poor prognosis. Staging and prognosis rely on positron emission tomography computed tomography (PET-CT). The International Prognostic Index (IPI) aids risk stratification. PET-CT is critical for assessing treatment response and guiding strategies. First-line management for LBCL can be informed by interim PET to assess chemosensitivity, with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) or polatuzumab vedotin rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (Pola-R-CHP) for advanced stages depending on IPI scores. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) management favors R-CHOP given every 14 days (R-CHOP14) or dose-adjusted etoposide, doxorubicin, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, prednisone, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) without radiotherapy in complete responders. Elderly patients, unfit or not (≥80 years or <80 with poor fitness), need geriatric assessment to guide therapy, often R-miniCHOP or non-anthracycline regimens. Frail patients should have adapted treatments. Prephase corticosteroids improve performance status, and supportive treatment should be optimized. The value of central nervous system (CNS) prophylaxis remains uncertain. CNS-IPI scores and specific anatomical sites help identify high-risk patients; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and colony-stimulating factor (CSF) analysis are recommended. Approximately 30%-40% of patients with LBCL experience relapsed or refractory disease after 1L treatment. Treatment strategies vary based on the timing of relapse (<1 year or ≥1 year). For those refractory or relapsing within <1 year and fit for therapy, chimeric antigen receptor T (CART) are the gold standard in 2L. CART in CART-naïve patients and bispecific antibodies appear to be the best approach in 3L. Follow-up includes clinical examination for 2 years and management for long-term side effects, such as cardiotoxicity, osteoporosis, immune dysfunction, neurocognitive impairment, endocrine dysfunction, fatigue, neuropathy, and mental distress.
© 2025 The Author(s). HemaSphere published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Hematology Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Catherine Thieblemont discloses a direct financial relationship (honoraria) with Janssen, Roche, AbbVie, Novartis, BMS, Incyte, and BeiGene. Maria Gomes Da Silva discloses financial and/or professional relationships with Janssen Cilag (Direct and Indirect), Roche (Direct), Lilly (Direct and Indirect), AstraZeneca (Indirect), Gilead (Direct), BeiGene (Indirect), AbbVie (Direct and Indirect), and Takeda (Direct), and professional relationships with Sociedade Portuguesa de Hematologia. Sirpa Leppä discloses a direct financial relationship with AbbVie, Genmab, Incyte, Roche, and Sobi, and an indirect financial relationship with Bayer, BMS, Genmab, Hutchmed, Novartis, and Roche. Georg Lenz discloses a direct financial relationship with Roche/Genentech, Gilead, BMS, Novartis, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Incyte, PentixaPharm, Sobi, Immogene/FLINDR, Hexal/Sandoz, Lilly, BeiGene, and MSD, and an indirect financial relationship with Roche/Genentech, Gilead, Bayer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, MSD, and Pierre Fabre. Armando Lopez‐Guillermo discloses a direct financial relationship with AbbVie, Atarabio, BMS, GenMab, Gilead/Kite, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly, Morphosys, Ono, Roche, SERB, SOBI, and Takeda, and an indirect financial relationship with BeiGene and AbbVie. Timothy Illidge discloses a direct financial relationship with Takeda. WJ discloses a direct and indirect financial relationship with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Janssen Cilag, Lilly, Regeneron, and Roche. Hans Eich discloses a direct financial relationship (honoraria) with Kyowa Kirin and Takeda and serve as a Steering Committee Member of the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group (ILROG). Igor Aurer discloses a direct financial relationship with Roche, Novartis/Sandoz, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Genesis/Incyte, Sobi, and Takeda. Marek Trneny discloses a direct financial relationship with Roche, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Sobi, Takeda, Incyte, Lilly, BMS, Novartis, AbbVie, Janssen, Swixx, Carbou Sciences, and Autolus. Andrew Davies discloses a direct financial relationship with Roche (conference attendance, honorarium for talks, advisory boards), AstraZeneca, Kite/Gilead, Sobi, AbbVie, Genmab, Celgene, MSD, Incyte, and Janssen (advisory boards), and an indirect financial relationship (research funding) with Roche, AstraZeneca, Kite/Gilead, Celgene, and MSD. Natacha Bolanos discloses an indirect financial relationship with Roche, Ipsen, Kite‐Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Sobi, Takeda, and BMS, as the Lymphoma Coalition has received sponsorship from these companies to support specific activities such as educational, advocacy initiatives, CABs, Global Patient Surveys, and Global Summits. Additionally, I am a member of the Patient Global Advisory Board for Ipsen. Martin Dreyling discloses a financial relationship through scientific advisory board honoraria with Abbvie, Astra Zeneca, AvenCell, Beigene, BMS, Genmab, Gilead/Kite, Incyte, Janssen, Lilly/Loxo, Novartis, Roche, Sobi; and research support (institution) Abbvie, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly, Roche. Umberto Vitolo discloses a direct financial relationship with AbbVie, Genmab, and Gilead (advisory board and lecture honoraria), as well as Incyte and MSD (lecture honoraria). Hervé Tilly discloses a direct financial relationship with Roche and an indirect financial relationship with Roche, AstraZeneca, BMS, and AbbVie. Marie‐José Kersten disclose an indirect financial relationship with Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotech, Novartis, Roche, Adicet Bio, AbbVie, BeiGene, Galapagos, Mustang Bio, and Janssen. Anne‐Ségolène Cottereau, Andy Andreas Rosenwald, Ben (Gerben) Zwezerijnen, Maja Marković, Jean‐Philippe Jais, Florence Broussais have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
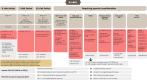
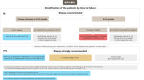
References
-
- Kanas G, Ge W, Quek RGW, Keeven K, Nersesyan K, Arnason JE. Epidemiology of diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL) in the United States and Western Europe: population‐level projections for 2020–2025. Leuk Lymphoma. 2022;63:54‐63. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
