NUFIP1-Mediated Ribophagy Alleviates PANoptosis of CD4+ T Lymphocytes in Sepsis via the cGAS-STING Pathway
- PMID: 40995563
- PMCID: PMC12454940
- DOI: 10.34133/research.0895
NUFIP1-Mediated Ribophagy Alleviates PANoptosis of CD4+ T Lymphocytes in Sepsis via the cGAS-STING Pathway
Abstract
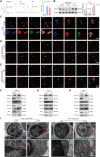
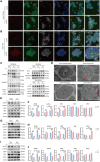
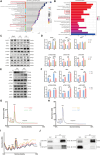
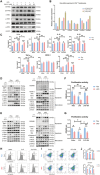
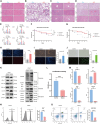
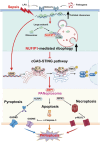
T lymphocyte dysfunction represents a pivotal determinant of immunosuppression in sepsis. Our previous studies demonstrated that nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1 (NUFIP1)-mediated ribophagy conferred cytoprotection against apoptosis in CD4+ T lymphocytes during sepsis, thereby preserving host immunocompetence. Despite growing evidence linking PANoptosis to the pathogenesis of various diseases, the potential role of ribophagy in modulating CD4+ T lymphocytes' PANoptosis in sepsis remains largely unclear. In the present study, we employed both lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Jurkat T cells and cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis models to demonstrate marked exacerbation of CD4+ T lymphocyte PANoptosis following NUFIP1 knockdown (KD), associated with impaired immune function, as evidenced by diminished cytokine production and T cell proliferation. Tandem mass tagging (TMT) proteomic analysis identified Z-nucleic acid binding protein 1 (ZBP1)-mediated PANoptosome formation and the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-stimulator of interferon genes (cGAS-STING) pathway as critical nodes in ribophagy-dependent cytoprotection. Mechanistically, sepsis-induced ribosome collision activated the cGAS-STING signaling axis, which in turn recruited NUFIP1 to STING protein complexes. Clinical analysis of septic patients revealed enhanced ribophagy and PANoptosis in peripheral blood CD4+ T cells, consistent with the experimental findings. These results suggest that NUFIP1-mediated ribophagy alleviates CD4+ T lymphocyte PANoptosis in sepsis via the cGAS-STING pathway, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting ribophagy and PANoptosis pathways to mitigate immune paralysis and improve the outcomes following septic insults.
Copyright © 2025 Pengyue Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Meyer NJ, Prescott HC. Sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2024;391(10141):2133–2146. - PubMed
-
- Du X, Dong Z, Yan Y, Gong Y, Yuan M, Ma C, Xu L, Qu Y, Qu M, Pan P, et al. Immunomodulatory nanozymes eradicate intracellular infections and rescue immunoparalysis for treating multidrug-resistant bacterial sepsis. Exploration. 2025;20250127.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

