Nipple Reconstruction Using FixNip NRI: A Novel Nipple Reconstruction Implant (First-in-human Trial)
- PMID: 40995572
- PMCID: PMC12456498
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000007103
Nipple Reconstruction Using FixNip NRI: A Novel Nipple Reconstruction Implant (First-in-human Trial)
Abstract
Background: Loss of a nipple after mastectomy can adversely impact a patient's body image. This trial evaluated the performance and safety of the FixNip Nipple Reconstruction Implant (NRI), a hypodermic nipple structure designed to provide a reliable option for nipple reconstruction.
Methods: Female patients 22-70 years of age with a history of breast cancer and at least 3 months postmastectomy were eligible. Nipple reconstruction with the FixNip NRI was performed. Patients were followed up for 12 months, with visits at 1 week, and 3, 6, and 12 months post surgery. Follow-up included safety evaluations, nipple projection measurements, and completion of BREAST-Q patient satisfaction questionnaires.
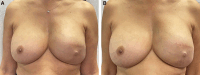
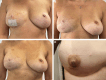
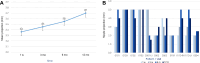
Results: Twelve FixNip NRIs were implanted in 10 patients. Nipple projection remained stable during 12 months, with mean ± SD projections of 3.4 ± 1.6 mm at 1 week and 3.7 ± 1.6 mm at 12 months. BREAST-Q questionnaires showed medium to high patient satisfaction. No intraoperative adverse events occurred, but 1 implant was removed due to postoperative infection and dehiscence.
Conclusions: FixNip NRI appears safe and feasible. Removal of the single implant may reflect the learning curve for patient selection and surgical technique. Use of this permanent implant maintained nipple projection for 12 months with medium to high patient satisfaction, suggesting promising outcomes for future reconstructions.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article. This study was supported by FixNip Ltd.
Figures



References
-
- Sherman KA, Woon S, French J, et al. Body image and psychological distress in nipple-sparing mastectomy: the roles of self-compassion and appearance investment. Psychooncology. 2017;26:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Fortunato L, Loreti A, Cortese G, et al. Regret and quality of life after mastectomy with or without reconstruction. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021;21:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Phoosuwan N, Lundberg PC. Life satisfaction, body image and associated factors among women with breast cancer after mastectomy. Psychooncology. 2023;32:610–618. - PubMed
-
- Didier F, Radice D, Gandini S, et al. Does nipple preservation in mastectomy improve satisfaction with cosmetic results, psychological adjustment, body image and sexuality? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;118:623–633. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
