Neurodevelopmental commonalities in cognitive control networks for mathematics and reading in meta-analysis of 3308 participants
- PMID: 40998771
- PMCID: PMC12462466
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63259-8
Neurodevelopmental commonalities in cognitive control networks for mathematics and reading in meta-analysis of 3308 participants
Abstract
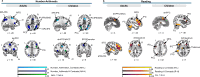
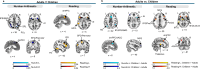
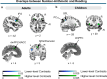
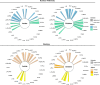
Mathematics and reading abilities are foundational academic skills that are robustly correlated across development, suggesting shared cognitive mechanisms. To identify their common neural architecture, we conducted the largest cross-domain meta-analysis to date (179 experiments, 3308 participants). By analyzing activation patterns across simple and complex tasks in both children and adults, we uncovered three key insights into how the brain supports academic performance and learning. First, while mathematical processing recruits frontal-parietal regions and reading frontal-temporal regions, both domains rely on shared cognitive control networks. The salience network in particular, anchored by the bilateral insula and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, supports both mathematical and reading processes, particularly during complex tasks. Second, children show broader engagement of these cognitive control networks than adults across both domains. Third, adults demonstrate more specialized posterior network engagement for domain-specific processing while maintaining prefrontal recruitment for challenging tasks, suggesting a developmental shift toward efficient, specialized processing. These findings suggest the ability to engage and coordinate cognitive control networks might represent a fundamental mechanism in academic performance and learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ritchie, S. J. and T. C. Bates, enduring links from childhood mathematics and reading achievement to adult socioeconomic status. Psychol. Sci. 24, 1301−8 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Duncan, G. J. et al. School readiness and later achievement. Dev. Psychol.43, 1428–1446 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Korpipää, H. et al. Early cognitive profiles predicting reading and arithmetic skills in grades 1 and 7. Contemp. Educ. Psychol.60, 101830 (2020).
-
- Ünal, Z. E. et al. What is the source of the correlation between reading and mathematics achievement? two meta-analytic studies. Educ. Psychol. Rev.35, 4 (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03 HD081087/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH084164/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- HD059205/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- HD094623/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 MH084164/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

