The distribution and the clinical importance of MUC5B and TERT variants in Turkish patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 40999395
- PMCID: PMC12465160
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03903-7
The distribution and the clinical importance of MUC5B and TERT variants in Turkish patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Background: The role of genetic variants in Mucin-5B (MUC5B) and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) pathogenesis, as well as their associations with clinical characteristics, remain uncertain and may exhibit ethnic variations.
Methods: This single-center, cross-sectional study aimed to investigate the distribution of MUC5B rs35705950 and TERT rs2736100 variants among Turkish IPF patients. Additionally, we assessed associations between these genetic variants and clinical parameters including gender-age-physiology (GAP) score, percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC%), percent predicted diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO%), and the presence of honeycombing on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT).
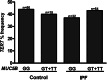
Results: The allele frequency of the TERT rs2736100 variant showed no significant difference between IPF patients and healthy controls (41.7% vs. 43.7%, OR = 0.92, p = 0.73). Conversely, the allele frequency of the MUC5B rs35705950 variant was significantly higher in IPF patients compared to controls (39.6% vs. 12%, OR = 4.81, p = 0.0001). IPF patients carrying the homozygous MUC5B variant (TT) exhibited significantly higher mean FVC% values than those without the variant (GG) (82.2% vs. 71.7%, respectively; p = 0.004). Furthermore, the mean age at diagnosis was significantly older in IPF patients carrying at least one T allele of the MUC5B variant (GT + TT) compared to non-carriers (GG) (67.7 years vs. 62.3 years, respectively; p = 0.013).
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the MUC5B rs35705950 variant is significantly associated with increased IPF susceptibility among Turkish patients. In contrast, the TERT rs2736100 variant was not linked to IPF risk. Additionally, the presence of the MUC5B rs35705950 variant correlated with later disease onset and relatively preserved pulmonary function in this patient population.
Keywords: Fibrosis; Genetic; Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF); Mucine-5B (MUC5B); Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT); Variant.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of Akdeniz University Faculty of Medicine on 21 November 2018 (Decision Number: 816). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to their inclusion in the study. The study was conducted in full accordance with the ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Financial support for the study was provided by the Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit (Project Number: TTU-2019-4793). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of Akdeniz University or any affiliated institutions.
Figures

References
-
- Borie R, Crestani B, Dieude P, Nunes H, Allanore Y, Kannengiesser C, et al. The MUC5B variant is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis but not with systemic sclerosis interstitial lung disease in the European Caucasian population. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70621. 10.1371/journal.pone.0070621. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- TTU-2019-4793/Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit
- TTU-2019-4793/Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit
- TTU-2019-4793/Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit
- TTU-2019-4793/Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit
- TTU-2019-4793/Akdeniz University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

