Fluorescent Peptide Tracers for Simultaneous Oxytocin Receptor Activation and Visualization
- PMID: 41001975
- PMCID: PMC12603982
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202515180
Fluorescent Peptide Tracers for Simultaneous Oxytocin Receptor Activation and Visualization
Abstract
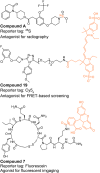
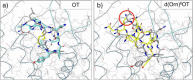
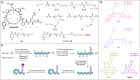
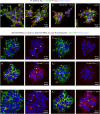
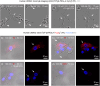
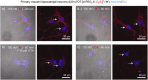
The oxytocin receptor (OTR) regulates critical physiological functions and has been implicated in a range of diseases, including psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorder. However, a lack of reliable molecular tools hampers the progress in understanding OTR's mechanistic roles in (patho)physiological processes. In this work, we addressed this gap and developed potent, selective, and bright fluorescent peptide tracers that enable precise spatial and functional investigations of OTR actions. Our tracers showed efficient OTR labeling, activation, and internalization in cellular bioassays in both live and fixed overexpression and primary cell systems, including those subjected to immunocytochemical protocols, highlighting their versatility as reliable new imaging tools. Additionally, they facilitated single-molecule tracking of OTR with live-cell super-resolution microscopy and were able to separate OTR-positive cells from mixed oxytocin and vasopressin receptor-containing cell populations via fluorescence-activated cell sorting, underscoring their wider scope for live-cell applications. In summary, we developed versatile fluorescent tracers based on the endogenous ligand oxytocin for both live-cell and post-hoc imaging that have additional functional capabilities beyond traditional antibody labeling, offering new avenues to explore OTR's role in health and disease.
Keywords: Bioactive peptide tracers; Imaging; Immunocytochemistry; Oxytocin receptor visualization; Structure–activity relationship (SAR) study.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The tracers developed are patented. All authors have read, commented on, and approved the manuscript and have not expressed any further conflicts of interest.
Figures
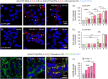
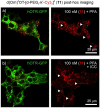
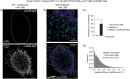
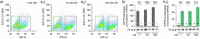
References
-
- Casadó V., Casadó‐Anguera V., Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2023, 18, 815–820. - PubMed
-
- Jurek B., Neumann I. D., Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1805–1908. - PubMed
-
- Perisic M., Woolcock K., Hering A., Mendel H., Muttenthaler M., Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 361–377. - PubMed
-
- Assinder S. J., Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2384, 1–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DP230102278/Australian Research Council
- LE130100078/Australian Research Council
- DP230102707/Australian Research Council
- FT210100266/Australian Research Council
- GNT#1155794/National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Fellowship
- DVCR22052A/The University of Queensland Strategic Initiatives Fund
- 714366/European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program
- 1146504/Cancer Council Queensland and Cancer Australia
- TAI 382-B/Austrian Science Fund (FWF)
- P34121-B/Austrian Science Fund (FWF)
- 10.55776/P36762/Austrian Science Fund (FWF)
- 27012/Austrian Academy of Sciences DOC Fellowship
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

