Genetic Deletion of RHAMM Alleviates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Reversing Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Elevation in Male Obese Mice
- PMID: 41002415
- PMCID: PMC12468513
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14181448
Genetic Deletion of RHAMM Alleviates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Reversing Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Elevation in Male Obese Mice
Abstract
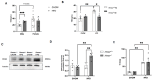
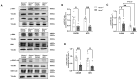
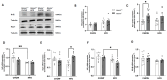
Objective: Obesity induces hypothyroidism with unknown mechanisms. This study investigates the role of (Receptor for Hyaluronan-Mediated Motility (RHAMM) in obesity-associated thyroid dysfunction, focusing on hepatic oxidative stress. Methods: Global RHAMM-deficient mice and their wildtype littermate controls were fed a normal chow diet or high-fat diet (HFD) for 16 weeks. Thyroid function was evaluated by measuring plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. The hepatic oxidative response was assessed by measuring signaling pathways associated with nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activity. Results: HFD feeding increased plasma TSH levels in male mice but not in female mice. RHAMM deletion in male mice mitigated HFD-induced TSH elevation, which was associated with enhanced hepatic antioxidant defenses and reduced inflammation. This was evidenced by elevated expression of the Nrf2 target gene NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (Nqo1), reduced protein carbonylation and nitration levels, and reduced expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α in livers of male RHAMM-deficient mice. Mechanistically, RHAMM deletion decreased AKT/ERK signaling, increased GSK3 signaling, increased CD44 protein expression, and increased Nqo1 levels in the liver. Conclusions: RHAMM promotes obesity-induced thyroid dysfunction by regulating oxidative stress and inflammation in male mice. Targeting RHAMM may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for mitigating obesity-related endocrine and metabolic disorders.
Keywords: Nrf2; RHAMM; obesity; oxidative stress; thyroid dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nabi G., Hao Y., Liu X., Sun Y., Wang Y., Jiang C., Li J., Wu Y., Li D. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis Crosstalk with the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis and Metabolic Regulation in the Eurasian Tree Sparrow During Mating and Non-mating Periods. Front. Endocrinol. 2020;11:303. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00303. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

