Changing Climate, Changing Candida: Environmental and Social Pressures on Invasive Candidiasis and Antifungal Resistance in Latin America
- PMID: 41003155
- PMCID: PMC12471215
- DOI: 10.3390/jof11090609
Changing Climate, Changing Candida: Environmental and Social Pressures on Invasive Candidiasis and Antifungal Resistance in Latin America
Abstract
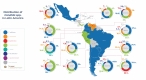
Invasive candidiasis (IC) in Latin America is undergoing a significant epidemiological shift, increasingly driven by non-albicans strains such as Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candidozyma auris. These pathogens often exhibit multidrug resistance, which complicates treatment and increases mortality. Diagnostic limitations, particularly in rural and public hospitals, delay detection and hinder the provision of rapid care. Environmental pressures, such as climate change and the widespread use of azoles in agriculture, appear to favor the selection of resistant and thermotolerant strains. Migratory birds may also play a role in the environmental transmission of pathogenic fungi. These factors are amplified by socioeconomic inequalities that restrict access to diagnostics and first-line antifungals. To help mitigate this emerging challenge, a One Health-oriented framework combining integrated environmental surveillance, robust antifungal-stewardship programmers, broader diagnostic access, and coordinated cross-sector public health actions should be developed. Reinforcing these pillars could lessen the regional burden of IC and slow the advance of antifungal resistance.
Keywords: Candidozyma auris; Latin America; antifungal resistance; climate change; invasive candidiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources