Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised Critically Ill Patients: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Clinical Features and Diagnosis-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 41003163
- PMCID: PMC12470843
- DOI: 10.3390/jof11090617
Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Immunocompromised Critically Ill Patients: Prevalence, Risk Factors, Clinical Features and Diagnosis-A Narrative Review
Abstract
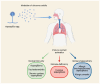
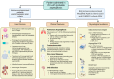
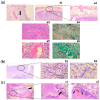
Aspergillosis in immunocompromised individuals is a serious and potentially life-threatening infection, as the weakened immune system cannot effectively fight the Aspergillus fungus. This review provides an in-depth examination of aspergillosis in patients with various conditions that compromise immunity, including hematological disorders, HIV, SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, influenza, and those who have undergone solid organ transplants. The clinical manifestations of aspergillosis are influenced by factors such as the host's underlying comorbidities, immune response, and immune suppression due to medications or treatments. The review delves into the epidemiology of aspergillosis, exploring various risk factors that predispose individuals to infection. It also discusses the wide range of clinical symptoms, highlighting the challenges in diagnosis and the importance of early detection. The review contrasts traditional diagnostic approaches with emerging molecular techniques, emphasizing the role of advanced diagnostics in improving outcomes. A proposed clinical decision-making flowchart is provided to assist healthcare professionals in managing suspected cases of aspergillosis. In addition to diagnostic challenges, the review addresses antifungal prophylaxis, pre-emptive therapy, and the growing concern of pharmacological resistance to antifungal agents. It concludes with a discussion of future research directions, underscoring the need for improved therapeutic strategies and preventative measures in immunocompromised patients to reduce the burden of this severe fungal infection.
Keywords: Aspergillus; antifungal treatment; immunocompromised patients; invasive aspergillosis; pulmonary aspergillosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Calderón-Parra J., Mills-Sanchez P., Moreno-Torres V., Tejado-Bravo S., Romero-Sánchez I., Balandin-Moreno B., Calvo-Salvador M., Portero-Azorín F., García-Masedo S., Muñez-Rubio E., et al. COVID-19-associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA): Risk Factors and Development of a Predictive Score for Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Mycoses. 2022;65:541–550. doi: 10.1111/myc.13434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

