STK11 coordinates IL-4 signaling with metabolic reprogramming to control M2 macrophage polarization and antitumor immunity
- PMID: 41004572
- PMCID: PMC12466853
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adx5495
STK11 coordinates IL-4 signaling with metabolic reprogramming to control M2 macrophage polarization and antitumor immunity
Abstract
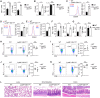
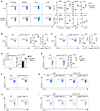
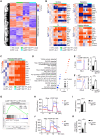
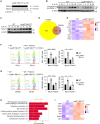
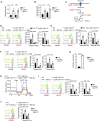
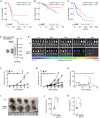
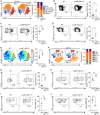
Macrophages integrate microenvironmental cues to orchestrate complex transcriptional and metabolic programs that drive functional polarization. Here, we demonstrate that STK11 links interleukin-4 (IL-4) signaling with metabolic reprogramming to restrain alternatively activated (M2) macrophage polarization. Through integrative transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses, we identified STK11 as a key transcriptional and metabolic regulator during M2 polarization. STK11 deficiency enhanced the expression of M2-associated markers and promoted glutamine metabolism in IL-4-stimulated macrophages. Mechanistically, STK11 deficiency led to increased FOXO1 activation, thereby promoting M2 polarization. Pharmacological inhibition of FOXO1 or glutamine metabolism effectively reversed the enhanced M2 polarization. In an orthotopic model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, myeloid-specific deletion of STK11 resulted in increased accumulation of M2-like tumor-associated macrophages, impaired antitumor immunity, and accelerated tumor progression. These findings uncover a previously unrecognized role for STK11 in modulating M2 macrophage polarization, offering mechanistic insights that may inform the development of immunometabolic therapies for pancreatic cancer.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

