Fe-electrocatalytic deoxygenative Giese reaction
- PMID: 41006263
- PMCID: PMC12475461
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-63515-x
Fe-electrocatalytic deoxygenative Giese reaction
Abstract
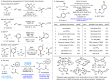
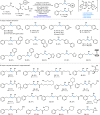
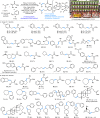
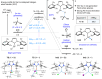
A redox-neutral Fe-electrocatalytic deoxygenative Giese reaction is reported. Hydroxyl groups are among the most abundant functional groups, and thus, the development of efficient reactions for their conversion has significant importance in medicinal and process chemistry. Here, we present a redox-neutral Giese reaction via anodic oxidation to generate phosphonium ions in combination with a cathodic reduction to yield low-valent Fe-catalysts. This reaction represents a promising example of a redox-neutral reaction using an Fe-catalyst and electrochemistry. The results obtained in this study will facilitate the exploration of a wide range of novel reactions employing this redox cycle in the future.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tsuji, J. Palladium Reagents and Catalysts: New Perspectives for the 21st Century 2nd ed. (Wiley, New York, 2004).
-
- Hartwig, J. F. Organotransition Metal Chemistry: From Bonding to Catalysis (University Science Books, New York, 2009).
-
- Gladysz, J. A. Introduction to frontiers in transition metal catalyzed reactions (and a brief adieu). Chem. Rev.111, 1167–1169 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Wang, Y., Xu, J., Pan, Y. & Wang, Y. Recent advances in electrochemical deoxygenation reactions of organic compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem.21, 1121–1133 (2023). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

