Immunological Targets in Generalized Myasthenia Gravis Treatment: Where Are We Going Now?
- PMID: 41008338
- PMCID: PMC12468546
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci15090978
Immunological Targets in Generalized Myasthenia Gravis Treatment: Where Are We Going Now?
Abstract
Background: Generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disorder marked by antibody-mediated disruption of neuromuscular transmission. Despite advancements in immunosuppressive therapies and biologics, a subset of patients remains refractory, necessitating more targeted and personalized treatment strategies.
Objective: This review aims to synthesize current knowledge of the immunopathological mechanisms across gMG subtypes and to explore emerging therapeutic targets tailored to these diverse disease phenotypes.
Methods: A narrative review was conducted, integrating recent findings from clinical trials, immunogenetic studies, and preclinical research to describe subtype-specific immune mechanisms and corresponding therapeutic innovations.
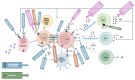
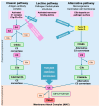
Results: gMG subtypes-characterized by autoantibody profiles (AChR, MuSK, LRP4, or seronegative), thymic histopathology, and age of onset-demonstrate distinct immunological pathways. Early-onset MG is associated with thymic hyperplasia and Th17-driven inflammation; thymoma-associated MG involves central tolerance breakdown; late-onset MG shows immune senescence and altered T-cell regulation. MuSK- and LRP4-positive MG exhibit unique cytokine and antibody signatures. Novel therapeutic strategies include B cell- and T cell-targeted therapies (e.g., anti-CD19, anti-CD38, JAK inhibitors), cytokine inhibitors (IL-6, IL-17, IL-23), FcRn antagonists, complement inhibitors, and gene- or cell-based therapies such as CAR-T and CAAR-T cells.
Conclusion: The evolving landscape of gMG treatment reflects a shift toward immunopathology-based precision medicine. Better characterization of subtype-specific molecular signatures and immune dysfunctions is essential to guide clinical decision-making and improve outcomes for treatment-refractory patients.
Keywords: autoantibodies; biological therapies; generalized myasthenia gravis; immunopathology.
Conflict of interest statement
ER received honoraria from UCB; LL received speaker honoraria and consultancy fees from argx; SM received public speaking honoraria and travel grants from Alexion; GA received conference honoraria, advisory board, and travel grants from Kedrion, Alnylam, Alexion, Argenx, and Takeda; LF received public speaking honoraria and/or advisory boards and travel grants from Alexion, Argenx, UCB, and Dianthus.
Figures
References
-
- McCallion J., Borsi A., Noel W., Lee J., Karmous W., Sattler S., Boggia G., Hardy E., Mitchell C., Mitchell S., et al. Systematic review of the patient burden of generalised myasthenia gravis in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. BMC Neurol. 2024;24:61. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03553-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

