Allosteric Control Overcomes Steric Limitations for Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Conserved Binding Epitopes of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Exploring the Intersection of Binding, Allostery, and Immune Escape with a Multimodal Computational Approach
- PMID: 41008647
- PMCID: PMC12466954
- DOI: 10.3390/biom15091340
Allosteric Control Overcomes Steric Limitations for Neutralizing Antibodies Targeting Conserved Binding Epitopes of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Exploring the Intersection of Binding, Allostery, and Immune Escape with a Multimodal Computational Approach
Abstract
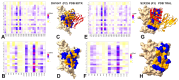
Understanding the atomistic basis of multi-layer mechanisms employed by broadly reactive neutralizing antibodies of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein without directly blocking receptor engagement remains an important challenge in coronavirus immunology. Class 4 antibodies represent an intriguing case: they target a deeply conserved, cryptic epitope on the receptor-binding domain yet exhibit variable neutralization potency across subgroups F1 (CR3022, EY6A, COVA1-16), F2 (DH1047), and F3 (S2X259). The molecular basis for this variability is not fully understood. Here, we employed a multi-modal computational approach integrating atomistic and coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations, mutational scanning, and dynamic network analysis to elucidate how these antibodies engage the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and influence its function. Our results reveal that neutralization efficacy arises from the interplay of direct interfacial interactions and allosteric effects. Group F1 antibodies (CR3022, EY6A, COVA1-16) primarily operate via classic allostery, modulating flexibility in RBD loop regions to indirectly interfere with the ACE2 receptor binding through long-range effects. Group F2 antibody DH1047 represents an intermediate mechanism, combining partial steric hindrance-through engagement of ACE2-critical residues T376, R408, V503, and Y508-with significant allosteric influence, facilitated by localized communication pathways linking the epitope to the receptor interface. Group F3 antibody S2X259 achieves potent neutralization through a synergistic mechanism involving direct competition with ACE2 and localized allosteric stabilization, albeit with potentially increased escape vulnerability. Dynamic network analysis identified a conserved "allosteric ring" within the RBD core that serves as a structural scaffold for long-range signal propagation, with antibody-specific extensions modulating communication to the ACE2 interface. These findings support a model where Class 4 neutralization strategies evolve through the refinement of peripheral allosteric connections rather than epitope redesign. This study establishes a robust computational framework for understanding the atomistic basis of neutralization activity and immune escape for Class 4 antibodies, highlighting how the interplay of binding energetics, conformational dynamics, and allosteric modulation governs their effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Omicron variants; SARS-CoV-2 spike protein; antibody binding; binding energetics; evolutionary mechanisms; immune escape; molecular dynamics; mutational scanning; protein stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Tai W., He L., Zhang X., Pu J., Voronin D., Jiang S., Zhou Y., Du L. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020;17:613–620. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

