Stroke in Dilated Cardiomyopathy: An Autopsy-Based Study of Mechanisms, Topography, and Clinical Implications
- PMID: 41008659
- PMCID: PMC12468113
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics15182287
Stroke in Dilated Cardiomyopathy: An Autopsy-Based Study of Mechanisms, Topography, and Clinical Implications
Abstract
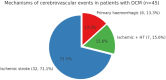
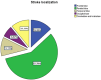
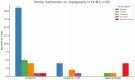
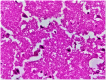
Background: Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a major cause of heart failure and arrhythmic mortality; yet, its association with cerebrovascular events, particularly in the absence of atrial fibrillation (AF), remains insufficiently explored. Purpose: This study aimed to determine the prevalence, mechanisms, and anatomical distribution of stroke in patients with DCM and to assess the role of AF and structural remodeling in stroke risk. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 471 patients who died with DCM at the Emergency County Clinical Hospital of Bihor between 1 January 2022 and 31 December 2024. Clinical records, neuroimaging, autopsy reports, and histopathological data were reviewed. Stroke subtypes were classified according to TOAST criteria (large artery atherosclerosis, cardioembolic, small vessel disease, other determined, undetermined) and hemorrhagic categories (intracerebral, subarachnoid). Demographic, echocardiographic, and comorbidity data were compared between patients with and without cerebrovascular events. Results: Of 471 patients with DCM, 45 (9.6%) had concomitant stroke: pure ischemic in 32 (71.1%), 7 (15.6%) showed ischemic with hemorrhagic transformation, and primary hemorrhagic in 6 (13.3%). The parietal lobe was most frequently affected. AF was present in 26 patients (57.8%) and was significantly associated with ischemic stroke (p = 0.004), though embolic strokes also occurred in sinus rhythm. Patients with stroke had significantly lower left ventricular ejection fraction (28.0 ± 13.7% vs. 34.0 ± 11.2%, p = 0.007) and larger atrial dimensions. Histopathological findings confirmed acute and chronic ischemic injury patterns, including "red neurons," white matter vacuolization, and gliotic scarring. Conclusions: Stroke is a frequent and often underdiagnosed complication in DCM, predominantly ischemic and embolic in nature. Importantly, embolic events were observed even in patients without AF, suggesting that atrial remodeling in DCM may independently predispose to cerebrovascular risk. These results underscore the need for refined preventive strategies, including careful atrial assessment and exploration of whether anticoagulation may benefit selected high-risk DCM patients without AF, a question that requires confirmation in prospective trials. Potential embolic sources in DCM include atrial cardiopathy and left ventricular thrombus in the setting of severe systolic dysfunction; therefore, careful ventricular as well as atrial assessment is warranted in high-risk DCM.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; autopsy; dilated cardiomyopathy; heart failure; histopathology; ischemic stroke; stroke; thromboembolic risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests relevant to the content of this manuscript. No financial, personal, or professional relationships influenced the design, execution, or interpretation of the study. The University of Oradea founded the Article Processing Charges (APC). The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

