Real World Data on the Efficacy of Brigatinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 41008926
- PMCID: PMC12468605
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers17183084
Real World Data on the Efficacy of Brigatinib in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
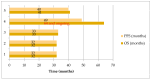
Introduction: Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer death among all cancers. The discovery of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) mutations led to an increased survival rate in patients with locally advanced and metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Results of the ALTA 1L study showed superior outcomes for patients treated with brigatinib compared to patients treated with crizotinib. Background: We conducted research including 23 patients with ALK-positive lung adenocarcinoma who were treated with brigatinib in first or further lines of therapy. The median follow-up was 22 months (4-66 months). Results: There were no significant differences in patient population between the first and further lines of treatment regarding sex distribution (p = 0.692), smoking status (p = 0.554), ECOG performance status (p = 1.000), and baseline presence of brain metastases (p = 0.862). The response rate was 47.8%, and disease control was 95.6%. The 12-month progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) rates were 85.3% and 86.5%, respectively, while the 60-month PFS rate was not reached, and the 60-month OS rate was 27.1%. The mPFS and mOS were 32 months. Conclusions: The results of this analysis are promising, as our patients experienced better outcomes compared to those in the ALTA 1L study, which may be attributed to the small sample size. However, the effectiveness of brigatinib has been confirmed in our clinical practice.
Keywords: ALK-positive; NSCLC; OS; PFS; brigatinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Solomon B.J., Mok T., Kim D.W., Wu Y.L., Nakagawa K., Mekhail T., Felip E., Cappuzzo F., Paolini J., Usari T., et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1408440. Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1582. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Camidge D.R., Kim D.W., Tiseo M., Langer C.J., Ahn M.J., Shaw A.T., Huber R.M., Hochmair M.J., Lee D.H., Bazhenova L.A., et al. Exploratory Analysis of Brigatinib Activity in Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases in Two Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:2693–2701. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.5841. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Costa D.B., Shaw A.T., Ou S.H., Solomon B.J., Riely G.J., Ahn M.J., Zhou C., Shreeve S.M., Selaru P., Polli A., et al. Clinical Experience with Crizotinib in Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:1881–1888. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.0539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

