Non-Electrophilic Activation of NRF2 in Neurological Disorders: Therapeutic Promise of Non-Pharmacological Strategies
- PMID: 41008955
- PMCID: PMC12466531
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14091047
Non-Electrophilic Activation of NRF2 in Neurological Disorders: Therapeutic Promise of Non-Pharmacological Strategies
Abstract
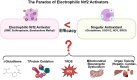
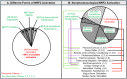
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) serves as a master transcriptional regulator of cellular antioxidant responses through orchestration of cytoprotective gene expression, establishing its significance as a therapeutic target in cerebral pathophysiology. Classical electrophilic NRF2 activators, despite potent activation potential, exhibit paradoxically reduced therapeutic efficacy relative to single antioxidants, attributable to concurrent oxidative stress generation, glutathione depletion, mitochondrial impairment, and systemic toxicity. Although emerging non-electrophilic pharmacological activators offer therapeutic potential, their utility remains limited by bioavailability and suboptimal potency, underscoring the imperative for innovative therapeutic strategies to harness this cytoprotective pathway. Non-pharmacological interventions, including neuromodulation, physical exercise, and lifestyle modifications, activate NRF2 through non-canonical, non-electrophilic pathways involving protein-protein interaction inhibition, KEAP1 degradation, post-translational and transcriptional modulation, and protein stabilization, though mechanistic characterization remains incomplete. Such interventions utilize multi-mechanistic approaches that synergistically integrate multiple non-electrophilic NRF2 pathways or judiciously combine electrophilic and non-electrophilic mechanisms while mitigating electrophile-induced toxicity. This strategy confers neuroprotective effects without the contraindications characteristic of classical electrophilic activators. This review comprehensively examines the mechanistic underpinnings of non-pharmacological NRF2 modulation, highlighting non-electrophilic activation pathways that bypass the limitations inherent to electrophilic activators. The evidence presented herein positions non-pharmacological interventions as viable therapeutic approaches for achieving non-electrophilic NRF2 activation in the treatment of cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative pathologies.
Keywords: NRF2; electrophilic; neurological disorders; neuromodulation; non-electrophilic; non-pharmacological intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lee J.-M., Calkins M.J., Chan K., Kan Y.W., Johnson J.A. Identification of the NF-E2-Related Factor-2-Dependent Genes Conferring Protection against Oxidative Stress in Primary Cortical Astrocytes Using Oligonucleotide Microarray Analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:12029–12038. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211558200. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shih A.Y., Johnson D.A., Wong G., Kraft A.D., Jiang L., Erb H., Johnson J.A., Murphy T.H. Coordinate Regulation of Glutathione Biosynthesis and Release by Nrf2-Expressing Glia Potently Protects Neurons from Oxidative Stress. J. Neurosci. 2003;23:3394–3406. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-08-03394.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

