Comprehensive Profiling of Cytokines and Growth Factors: Pathogenic Roles and Clinical Applications in Autoimmune Diseases
- PMID: 41009491
- PMCID: PMC12469660
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26188921
Comprehensive Profiling of Cytokines and Growth Factors: Pathogenic Roles and Clinical Applications in Autoimmune Diseases
Abstract
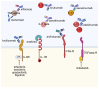
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by dysregulated adaptive immune responses leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Cytokines and growth factors play central roles in modulating immune regulation, inflammation, and tissue repair, thereby representing critical biomarkers for the enhancement of diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic monitoring. This review provides a comprehensive overview of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, as well as growth factors, emphasizing their pathogenic roles and clinical relevance across various autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and connective tissue diseases such as systemic sclerosis, Sjögren's syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Key pro-inflammatory cytokines-such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ-are examined regarding their contributions to disease progression and activity, alongside anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and IL-4, which regulate immune tolerance and inflammation resolution. Growth factors, such as TGF-β, are analyzed for their dual roles in immune modulation, fibrosis, and tissue remodeling. Cytokine signature profiles employed as diagnostic tools are discussed, together with the need for assay standardization. Advances in multiplex and omics technologies facilitating biomarker discovery are also reviewed. Finally, current and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting cytokines and growth factors, such as anti-TNF agents, IL inhibitors, anti-interferon therapies, and JAK/STAT pathway blockers, are explored.
Keywords: autoimmune diseases; cytokines; growth factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

