Copper, Cuproptosis, and Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 41009734
- PMCID: PMC12470802
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26189173
Copper, Cuproptosis, and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
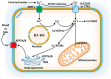
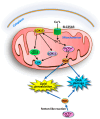
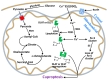
Copper is a vital micronutrient for animals and plants acting as a crucial cofactor in the synthesis of numerous metabolic enzymes and contributing to mitochondrial respiration, metabolism, oxido-reductive reactions, signal transmission, and oxidative and nitrosative damage. In the cells, copper may exist in the Cu+ and Cu++ oxidation states and the interconversion between these two states may occur via various redox reactions regulating cellular respiration, energy metabolism, and cell growth. The human body maintains a low level of copper, and copper deficiency or copper excess may adversely affect cellular functions; therefore, regulation of copper levels within a narrow range is important for maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Recent studies identified a new copper-dependent form of cell death called cuproptosis. Cuproptosis occurs due to copper binding to lipoylated enzymes (for instance, pyruvate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) in the tricarboxylic acid Krebs cycle. In recent years, extensive studies on copper homeostasis and copper-induced cell death in degenerative disorders, like Menkes, Wilson, Alzheimer, Parkinson's, Huntington's diseases, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, have discussed the therapeutic potential of targeting cuproptosis. Copper contamination in the environment, which has increased in recent years due to the expansion of agricultural and industrial activities, is associated with a wide range of human health risks. Soil used for the cultivation of grapes has a long history of copper-based fungicide application (the Bordeaux mixture is rich in copper) resulting in copper accumulation at levels capable of causing toxicity in plants that co-inhabit the vineyards. Phytoremediation, which uses plants and biological solutions to remove toxic heavy metals and pesticides and other contaminants from soil and water, is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective technology used for the removal of copper. It requires plants to be tolerant of high levels of copper and capable of accumulating metal copper in plants' aerial organs and roots. This review aims at highlighting the importance of copper as an essential metal, as well as its involvement in cuproptosis and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: chelating drugs; copper; copper homeostasis; cuproptosis; mitochondria; neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

